5. Dural Venous Sinus Flashcards
(34 cards)
three dense regular connective tissue layers that separate the soft tissue of the brain from the bones of the cranium
cranial meninges
functions of the cranial meninges
- encloses and protect blood vessels that supply the brain
- contain and circulate CSF
- some parts form veins that drain blood from brain
3 cranial meninges
- dura mater
- periosteal dura
- meningeal dura
- arachnoid mater
- pia mater
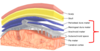
- tough membrane composed of 2 fiborus layers
- strongest of the meninges
- composed of 2 layers: (1) periosteal layer and (2) meningeal layer
dura mater
areas where the meningeal and the periosteal layers separate to form large, blood-filled spaces
dural venous sinuses
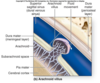
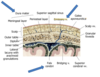
Identify the blue boxes.

- dura mater (meningeal and periosteal layers)
- falx cerebri
- emissary vein
- immediate internal to the dura mater
- composed of delicate web of collage and elastic fibers
arachnoid mater
arachnoid trabeculae
web of collagen and elastic fibers in arachnoid mater
between arachnoid and overlying dura mater
subdural space
immediately deep to the arachnoid
subarachnoid space
- innermost of the cranial meninges
- thin layer of delicate CT tightly adheres to brain & follows every contour of brain surface
pia mater
4 cranial dural septa
- falx cerebri
- tentorium cerebelli
- falx cereblli
- diaphragma sellae

extensions of the meningeal layer of the dura mater deep into the cranial cavity
cranial dural septa
functions of the cranial dural septa
separate specific parts of the brain and provide stabilization and support
sinuses found within the cranial dural septa

- superior sagittal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- transverse sinus

Identify the following septa.
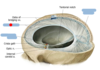
- (red) falx cerebri
- (under red) diaphragma sellae
- (right) tentorium cerebelli
piece of dura mater superior to the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone and pituitary gland
diaphragm sellae

What artery supplies the meninges?
middle meningeal artery (branches)
[ECA > maxillary a. > middle meningeal a. > passes through foramen spinosum]

branches of the middle meningeal artery
- frontal branch
- parietal branch
- mastoid branch
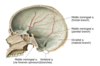
innervation of the meninges
- anterior meningeal branches of ethmoidal nerve (CN V1)
- meningeal branch of maxillary nerve (CN V2)
- meningeal branches of mandibular nerve (CN V3)
- tentorial nerve [recurrent meningeal branch of ophthalmic nerve] (CN V1)

Identify:
(1) area in purple
(2) area in blue
(3) area in pink
(4) area in orange
(5) gray boxes

- innervated by ophthalmic nerve (V1)
- innervated by maxillary nerve (V2)
- innervated by mandibular nerve (V3)
- innervated by cervical spinal nerves (C2-C3)
- anterior menineal branches of ethmoidal nerve, meningeal branch of maxillary nerve, meningeal branches of mandibular nerve, tentorial nerve (recurrent meningeal branch of ophthalmic nerve)
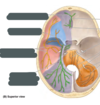
Label the figure.
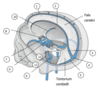
- superior sagittal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- straight sinus
- confluence of sinuses
- transverse sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- cavernous sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- posterior intercavernous sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- inferior petrosal sinus

Label.


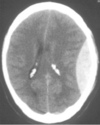
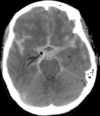
epidural hematoma

middle meningeal artery