12. Eye and Eye Movements Flashcards
bones of the orbit
- frontal
- ethmoid
- sphenoid
- zygomatic
- lacrimal
- maxillary
sinus relationships of the eye
- frontal
- ethmoid
- maxillary
in what direction does an orbital wall blow-out fracture typically occur
medially and inferiorly (involving maxillary bone)
- caused by indirect trauma
- orbital contents may prolape and become entrapped in maxillary sinus
- diplopia, globe ptosis, exophthalmous
orbital blowout fx
axes of the orbit diverge at a ___ degree angle
45
on what axis does abduction/adduction occur?
vertical axis
on what axis does elevation or depression occur?
horizontal axis
on what axis does medial rotation/lateral rotation occur?
AP axis
elevates the superior eyelid
levator palpebrae superioris m.
abducts, depresses, medially rotates eyeball
superior oblique m.
abducts, elevates, and laterally rotates eyeball
inferior oblique m.
elevates, adducts, and rotates eyeball medially
superior rectus m.
depresses, adducts, and rotates eyeball laterally
inferior rectus m.
adducts eyeball
medial rectus m.
abducts eyeball
lateral rectus m.
When the eye is abducted by the lateral rectus, what muscles produce elevation and depression?
superior and inferior rectus, respectively
When the eye is adducted by the medial rectus, only what muscles can produce elevation and depression?
oblique muscles
main arterial supply of eye and its origin
ophthalmic a. comes from ICA
Where do the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins drain into?
cavernous sinus
vascular structure encircling anterior chamber of eyeball through which aqueous humor is returned to the blood circulation
scleral venous sinus
- head tilts away from affected side
- diplopia worse on downward gaze
trochlear palsy

cannot look laterally w/ affected eye
abducens palsy

“down and out eye”
loss of ocular innervation
SO and LR intact
*type of oculomotor palsy*
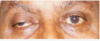
loss of innervation to levator palpebrae superioris m.
complete ptosis
*type of oculomotor palsy*














