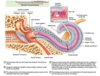
16. Ear Anatomy and Histology Flashcards
external ear
auricle to the tympanic membrane
middle ear
tympanic membrane to oval window
inner ear
oval window to internal acoustic meatus
Label external ear.


external ear blood supply
external carotid artery
[posterior auricular a. & superficial temporal a.]
cellular makeup of external ear
cartilage covered by integument

external ear sensory innervation

sensation to the external ear canal

histology of the external acoustic meatus
- outer 2/3: soft connective tissue & certilage
- inner 2/3: skin and bone
only place in the body where skin, periosteum, and bone exist directly on top of each other
external acoutic meatus (external auditory canal)
cell type of outside layer of tympanic membrane
stratified squamous epthelium
cell type of inside layer of tympanic membrane
simple cuboidal epithelium
describe tympanic membrane structure
- has concavity, cone-shaped oriented toward extenral acoustic meatus called umbo
- has flaccid part and tense part
- moves with sound and transmits to ossicles
Where is the middle ear (tympanic cavity) located?
petrous portion of temporal
2 parts of the middle ear
- tympanic cavity proper (mesotympanum)
- epitympanic recess (attic)
walls of the middle ear (tympanic cavity)
- roof: tegmental wall and jugular wall
- lateral: membranous wall
- medial: labyrinthine wall
- posterior: mastoid wall
- anterior: carotid wall
prominences of the anterior wall of middle ear
- lateral semicircular canal
- facial nerve
- labyrinth wall (promontory)
connects tympanic cavity (middle ear) with nasopharynx (back of the throat)
pharyngotympanic tube
cell type of pharyngotympanic tube
posterior lateral part (2/3) is bone but remainder (1/3) is cartilaginous
[note this is opposite of the external auditory meatus]
function of pharyngotympanic tube
equalize pressure [ear popping]
muscles that expend the pharyngotympanic tube
- levator veli palatini m.: contracts lognitdunally which pushes against one wall
- tensor veli palatini m.: pulls against another wall
Name the 3 auditory ossicles.
- malleus
- incus
- stapes
bridge the tympanic membrane with the oval window of the cochlea
auditory ossicles

tensor tympani m.
[origin, insertion, innervation, action]