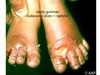
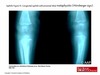
Week 4: Congenital infections Part I Flashcards
What is horizontal transmission?
Person-to-person
What is vertical transmission?
mother-to-child
Types of vertical transmission
3 listed
- Intrauterine
- Intrapartum
- Post-partum
What is intrauterine vertical transmission?
before birth- transplacental
What is intrapartum vertical transmission?
during the birth process
What is post-partum vertical transmission?
breastfeeding
Perinatal vertical transmissions
- Intrauterine
- Intrapartum
- Post-partum
Congenital vertical transmissions
Intrauterine
Describe the forms of vertical transmission and routes of transmission

How long is the neonate period?
First 28 days of life
Neonate immune system
immunocompromised
The immune system is still developing
- Global: all aspects of immune system
- Deficiency is inversely related to gestational age and birth weight
- Premature infants: Transplacental maternal IgG - doesn’t begin until 28 weeks gestation
When does transplacental maternal IgG begin
doesn’t begin until 28 weeks gestation
TORCH AKA

Incidence of Chlamydia per 1000 live births
150
Incidence of Chlamydia Number per year
593,637
Incidence of CMV per 1000 live births
10
Incidence of CMV Number per year
39,576
Incidence of Sepsis per 1000 live births
4
Incidence of Sepsis Number per year
15,830
Incidence of HSV, Toxo, VZV per 1000 liver births
1
Incidence of HSV, Toxo, VZV Number per year
3,958
Incidence of HIV per 1000 live births
0.5
Incidence of HIV Number per year
1,979 (53 in 2011)
Incidence of Congenital Syphilis per 1000 liver births
0.14