Ultimate Design Patterns - Behavioral Flashcards
(94 cards)
What are we going to learn in this course?
How to design re-usable, extensible software
What is not covered in this course?
No algorithms, no loops, no if statments, no logic
These topics are covered in other courses
We are not building an application!
Our focus is on building re-usable, easily extensible software
What must every software engineer working with object oriented systems know?
How to structure classes so they can collaborate
How to design software that can be easily extended
Twenty-three classic design patterns (creational, relational, behavioral) all software engineers must know!
How to design reusable and extensible object-oriented software
Master these!
What has helped Mosh tremendously when learning new frameworks?
Knowing design patterns
Sees these patterns repeated in various frameworks and libraries
Every new syntax looks similar to him!
What are design patterns?
Solutions to repeating features in software design
Design pattern shows us how to structure classes and how they communicate
Example
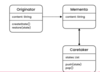
Undue feature (Memento Pattern) is a repeating feature in software design
What design patterns are covered?

Gang of Four Patterns
23 design patterns across creational, structural and behavioral domains
Creational - different way to create objects
Structural - relationships between objects
Behavioral - communication or interaction between objects

What are some of the benefits to mastering the classic design patterns?
- Can communicate without other developers - express your ideas abstractly using design patterns
- Makes you a better designer - Know how to build reusable and maintainable software no matter the language or framework you use!
- learn new frameworks faster - design patterns are used in different frameworks and languages, knowing them helps you learn them faster!
How should we take this course?
Take it beginning to end
Various principles are discussed in each section
What is a design smell?
overly complicated design
Many moving parts
design patterns applied without context
What is the focus of this course?
The art of designing object oriented software
Patterns ordered to teach us important concepts
What happens if we blindly apply design patterns to our applications?
Going to increase complexity
Now more moving parts
Haven’t solved the problem
Created an overly complicated design
aka “design smell”
What does a real engineer do?
- Try to understand the problem
- Brainstorm various solutions
- Pick the one that best fits the problem
How we should engineer software
Apply design patterns
What are the Behavior Design Patterns?

All about interaction (communication) between classes

What are the Structural Design Patterns?
All about the relationship between classes

How should we apply design patterns?
- Try to understand the problem
- Brainstorm various design pattern solutions
- Pick the design pattern that best fits the problem
What do code monkeys do?
Write code
Not understanding the problem they are trying to solve
What is abusing design patterns?

A few decision making statements in a single place, nothing wrong!
In State pattern, had decision making statements in multiple methods AND to support a new tool had to modify code!
All decision making was in single place, will not have a new state in the future so no maintainability or extensibility issues!
Code is now overly complicated without benefits
More moving parts
Logic spread over two classes!
What did Leonardo DaVinci say?
Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication
What should we not do?
Abuse design patterns!
Use them without understanding the problem, context and the various solutions!
Use them to improve extensibility and maintainability NOT to make complex applications with no additional benefts!

What is a tightly coupled application?
One in which all the classes are dependent on eachother!
If you change one class, cascading changes happen in other classes
Ex. If you get a flat tire, you only replace one tire
Not all the other tires, the engine and the seatbelt
A car is loosely coupled. Each part isn’t dependent on the other parts.
How can we build loosely coupled applications?
Using interfaces!
Components work together but are not dependent on eachother!
Can replace individual parts separately!
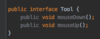
What are interfaces?
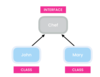
A contract that specifies the capabilities that a class should provide as services
Highly misunderstood construct in Java and other languages!
Ex. Open a restaurant, need a cheff
Not dependent on a particular cheff, just someone with the particular capabilities
This is a loosely coupled system!
Represent role of a cheff as interface
actual cheffs, classes that implement cheff interface
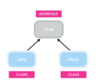
When should we use an interface vs. abstract class?
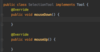
allow us to build loosely coupled applications!
Use abstract class if want to provide common code to child classes
methods in an interface are considered abstract (cannot instantiate them) so can omit abstract keyword
What is the open close principle?
Very important!
Open for extension - can add new classes
Closed for modification - cannot change code in classes
Support new feature?
add new classes, test them!
Makes application robust and extensible