Algorithms Flashcards
(73 cards)
What key algorithms does this course explore?
Search, Sort, String Manipulation
These algorithms up in software engineering interviews all the time!
What distinguishes an average programmer from an outstanding software engineer?
Understanding how search, sort and string manipulation algorithms work and evolved distinguishes an average programmer from an outstanding software engineer!
Why?
Libraries and frameworks helps us sort data without knowing how sorting or searching algorithms work!
So…
That’s why sorting algorithms come up in interviews all the time!
Action:
How they work, Time & Space complexity, implementation
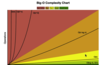
What algorithms run in good Big-O?
algorithms that run in green or yellow!
What are the seven essential sorting algorithms all software engineers must know?
- Bubble Sort
- Selection Sort
- Insertion Sort
- Merge Sort
- Quick Sort
- Counting Sort
- Bucket Sort
What must we be able to do with sorting algorithms?
Explain how each algorithm works
Know each algorithm’s time and space complexities
Implement each algorithm in given language of choice (Java)
What is bubble sort?
sort in increasing order (ascending order)
scan array from left to right, if out of order, swap
if right is smaller than left, swap them
requires multiple passes (iterations)
next largest number moves to correct position

What is the Big-O for bubble sort?
Best case = already sorted
worst case = reverse sorted
O(n) * O(n) = quadratic (worst case)
O(n) = linear (best case)
passes = each pass bubble one number into place
comparisions = bubbling into place

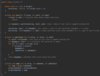
How do we implement bubbleSort( ) in Java?
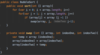
How can we optimize our implementation of bubblesort( )?

reduce O(n) iterations if sorted!
compare only unsorted items by not comparing last items (bubbled up items)

What is selection sort?
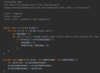
ascending order (smallest to largest)
Multiple passes over an array
In each pass we select the minimum value (from unsorted part) and swap this index with next index(in sorted part).

What is the time complexity of the selection sort algorithm?
O(n) * O (n) : Quadratic
Fairly slow algorithm!
iterate array = O(n) operation!
iterate unsorted array = O(n) operation!
next min value - iterate unsorted part = O(n)

How do we implement selectionSort ( ) using java?
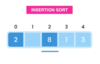
What is insertion sort?
each iteration pick one value from unsorted part, insert into sorted part (shift, make space)
Insert how?
We copy the values in the sorted part to the right to make space, then insert the value into the correct position.
Current (unsorted min value) is compared to all values in sorted part.
greater values are shifted to make space.

What is the key difference about insertion sort vs. bubble sort and selection sort?
instead of swapping items, we shift items in our array to the right
What is the Big-O for insertion sort?
O (n) * O (n) - quadratic
(worst case)
Same as bubbleSort( )!

How do we implement insertionSort( ) in java?

What is merge sort?
n (log n) time complexity!
Why?
It’s a type of algorithm called “divide and conquer algorithm.”
How?
it works by breaking the problem down into recursively smaller problems that are easy to solve.
Then it merges those solutions to get the final result.
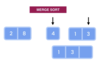
How does merge sort work?
dividing and conquering!
break array at middleIndex
divide again at middleIndex (left subarray)
divide again at middleIndex (right subarray)
keep breaking down the array into smaller subparts.
Until, cannot divide anymore
Then compare subparts and merge (sorted)
What is the Big-O of the merge sort algorithm?
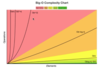
Time complexity:
O(n log n) operation!
O (log n) - dividing into subparts
O(n) - read each item, merge subparts
Faster than quadratic!
Space complexity:
O (n) space!
Don’t need to re-create arrays for merge, reuse

How do we implement MergeSort algorithm in Java?
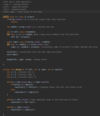
How do we implement a base condition to stop recursion in merge sort?
if their is one item in the array only!
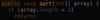
What is partitioning?
How we move items around a pivot
How?
select last item as pivot
rearrange other elements around it
using two pointers
i = iterate over array (loop variable)
b = boundary (end of left partition)
if the item is smaller than the pivot…
increase boundary (left partition), we swap lower value into left partition

What is the quickSort algorithm?
One of the most used sorting algorithms
built into many frameworks and languages
Why?
sorts an array in place without additional space.
O (log n) average time complexity!
How?
first, select a pivot
re-order the items around this pivot (partitioning)
items on right are larger than pivot
items on left are smaller than pivot
Pivot is now in place (doesn’t move)
select next item as pivot
partition again

What is the Big-O of the quick sort algorithm?
Why?
O(n) - have to iterate all items and swap (partitioning)
# of times can partition - depends on pivot selection
w/ the right pivot selection on average can run in
O(log n) time