OOP_Java Flashcards
(185 cards)
What must we know about Java before fully being able to implement OOP in Java?
Know Java basics!
This course has intermediate topics!

What are the styles of programming used in computer science?
Object-oriented and functional are the two most popular used today!

What are programming paradigms?
They are styles of writing code.
OOP, Procedural, Functional
Many languages support multiple paradigms.
Not languages!
Ex. Python, Ruby, Java, Javascript

Which programming languages support multiple programming paradigms?
OOP, Procedural, Functional:
Python, Ruby, Javascript, Java

What is everything based on in object-oriented programming (OOP)?
Everything is based on the concept of objects
The objects are units that contain:
data
methods (behaviors) that act on the data

What is the challenge with OOP?
It’s fairly complex.
Many books fail to explain it properly.
What is an object?
Units that contain:
data (state)
operations on data (behavior) - methods/functions
Together in a single unit
Describe functional programming
vs. OOP?
Functional:
Data (fields)
Behavior (methods/functions)
*Completely independent of each other
OOP:
Data (fields)
Behavior (methods/functions)
*Grouped together in Units
Which style of programming is the best?
It depends on the type of problem you are trying to solve!
Some paradigms make more sense in a given context
No paradigm works best in all situations.
Every problem is different.
It all depends on the problem, context, budget
Ex.
Some make the mistake to try to solve all problems in one style or way of programming (OOP vs. functional).
What is a problem in the software industry?
Engineers are more excited about new languages and features than actually solving problems.
They think they know how to solve problems when actually they don’t!
What is problem-solving?
The definition of engineering problem-solving.

When is Object-Oriented Programming a better choice?
Graphical user interfaces and games!
When is functional programming a best choice?
In applications that require a high amount of reliability.
Problems that involved messages that get passed around and transformed along the way.
When might our application use different paradigms in a single application?
the event-driven paradigm in parts that make sense
functional or object-oriented paradigm parts that make sense.

Is there a one-size-fits-all for software engineering?
No!
Every problem is different.
depends on the project, the context, and the budget!
What is object-oriented programming?
A programing paradigm that groups data and methods that act on the data together in objects.
Object-oriented programming is about objects.
These objects interact with each other to perform various tasks!
Ex.
A car consists of thousands of collaborating objects that are reusable and replaceable!
What are the benefits of OOP?
Ex.
We can break a large application into smaller parts, we can focus on code for that object.
Fix the object or plugin another object.

What is covered in this course?
Classes - building blocks of OOP
What they are, how to build them
Encapsulation
Abstraction
Refactor Mortgage calculator to OOP
Inheritance & Polymorphism
Interfaces - coupling problems
JDK classes + frameworks

What is the most important section of this course?
The exercise of refactoring code into OOP format is a crucial skill all Java developers must have!
hardcore coding techniques NOT found in any other courses.
Taking procedural code and refactoring into OOP

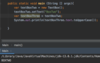
What does refactoring procedural code into OOP look like?
Procedural:
A bunch of methods calling each other in one main class!
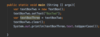
OOP:
Use abstraction
Use encapsulation
Use inheritance
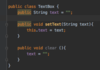
What is covered on classes in Java?
Encapsulation
Abstraction
Constructors
Getters/Setters
Method Overloading
*Many of these concepts are misunderstood by developers

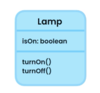
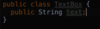
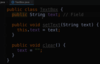
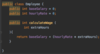
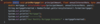
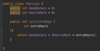
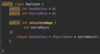
What is a class?
A template or blueprint for creating objects.
The fields are variables storing data
The methods act on the data values
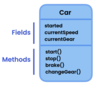
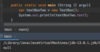
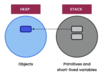
What is an object?
An instance of a class
independent of each other.
Stored in separate memory locations
Can be in its own state
Ex.
Current speed vs. Current Gear
different in each car object
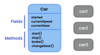
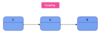
What is UML?
A simple visual language we use to show classes and their relationships
Unified modeling language
visualize classes