Non-Linear Data Structures Flashcards
(170 cards)
What is Big O notation?
Big O is a mathematical notation
Time/space complexity
that describes the limiting behavior of a function where the argument tends toward a particular value or infinity.
When do we use Big O notation?
To determine the scale-ability of an algorithm as input grows large.
What does Big O describe?
The performance on an algorithm
What does Big O have to do with data structures?
Certain operations can be more or less costly depending on what data structure is used (Array, Linked List, Queue, etc)
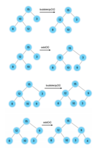
Name the different time complexities.

What is exponential time complexity?
The opposite of logarithmic time complexity.
The exponential curve grows faster as the input grows.
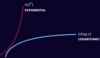
Which is time complexity more efficient?
log(n)
O(n)
While O(n) grows linearly with greater input,
O(log n) slows down at some point.
This makes O(log n) quadratic time more efficient that O(n) linear time.
At what point does the logarithmic algorithm slow down?
at some point, O(log n) will slow down.
When we reduce our work in half every step.

What is the Big-O for linear search vs. binary search?
linear search = O(n).
Iterate an array.
binary search = O(log n).
search a binary tree.
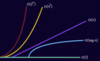
What are the five most common time complexity curves?
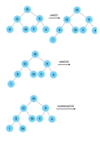
What are non-linear data structures?
- Binary Trees
- AVL Trees
- Heaps
- Tries
- Graphs
When would we have a quadratic Big-O value?
When we use nested loops that each performs an iteration over the entire set of values.
What is logarithmic time complexity?
When we throw out half our items and narrow our search.
o(log n) - binary search tree lookup
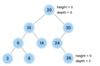
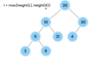
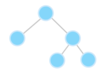
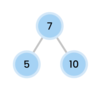
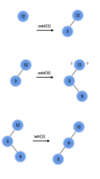
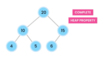
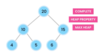
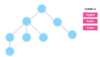
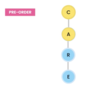
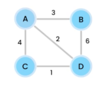
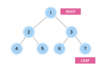
What is a tree?
A nonlinear data structure
stores elements in a hierarchy.
The “elements” are referred to as “nodes.”
Each “node” has data or values (could store objects).
The “lines” that connect “nodes” are called “edges.”
What are real-world applications of trees?
Tons of applications
databases
graphical user interfaces
websites
- Hierarchical data (files, folders) - File systems on your computer
- Databases (indexing) - use trees for indexing for fast database lookup.
- Autocompletion (matching previous queries) - Storing old search queries in a tree than trying to match old search queries to new entries.
- Compilers (translate code into new languages)
- Compression algorithms (JEPG, MP3)
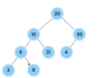
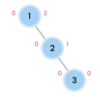
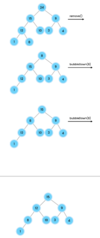
What is special about a binary tree?
Allows for logarithmic time complexity
left subtree is smaller than root
right subtree is greater than root
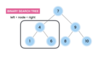
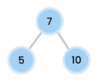
What is the top node of a tree called?
The top node is a tree is called “the root.”
The root node has two children in a binary tree.
What are the children nodes called in a tree?
The children nodes of a root node are called “leaves.”
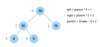
What is the run time complexity of various operations on binary trees?
Logarithmic time complexity
Lookup ( ) : O(log n)
addItem ( ) : O (log n)
deleteItem ( ): O (log n)
**if a tree isn’t set up properly the performance may degrade to O(n).

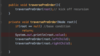
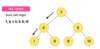
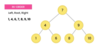
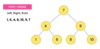
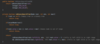
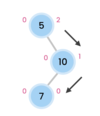
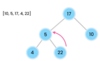
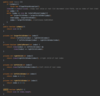
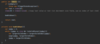
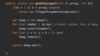
What values are we going to use for our binary search tree algorithm implementation?
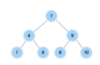
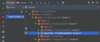
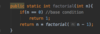
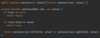
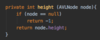
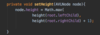
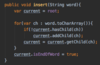
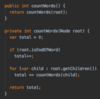
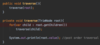
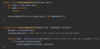
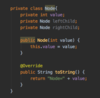
How do we implement the Node { } class in our binary tree?
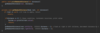
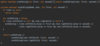
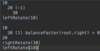
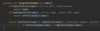
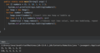
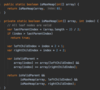
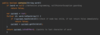
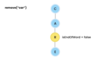
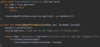
How do we implement the addItem( ) method in our binary search tree?
O ( log n ) operation!

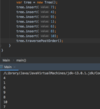
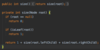
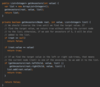
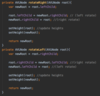
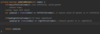
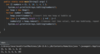
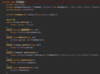
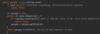
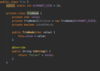
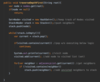
How do we implement the lookup( ) method in our binary tree?
O(log n) time complexity
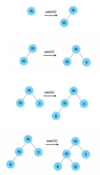
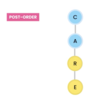
Traversal:
Root, leftChild, rightChild
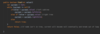
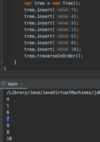
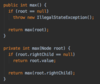
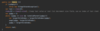
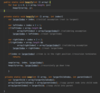
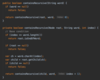
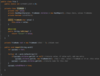
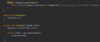
How do we implement a recursive method for printing nodes in traversePreOrder ( )?
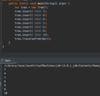
Kick off recursion with method overloading
End with base condition