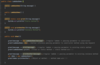
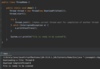
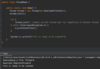
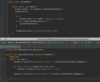
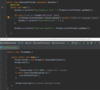
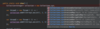
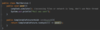
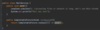
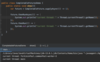
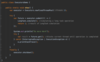
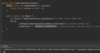
Java_advanced Flashcards
(235 cards)
What does this course cover?
Topics advanced Java developers use a daily basis.
Designed as a step by step guide and reference.
Each section builds on top of itself.

What are the requirements?
Should know the basics of OOP in Java!
Start from part 1 or part 2 of the series!
Or you’ll find the topics difficult to understand!

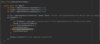
What is covered in the exceptions section?

What is the root cause of many problems in Java programs?
NullPointerException
A class declared in java.lang package
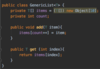
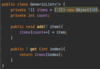
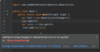
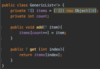
What is an exception?
An object that contains information about an error
Several exception classes
What should a good Java developer anticipate?
Exceptions and handle them!
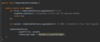
What are the three types of exceptions in Java?
Checked Exceptions :

Exceptions we as developers should anticipate and handle
Exceptions forced to handle by Java compiler
Checked at compile time by java compiler (red underline)
Ex. Handle edge cases vs. runtime terminating program
Unchecked (runtime exceptions) :
not checked during compile time by Java Compiler
due to programming errors
Ex. NullPointerException due to trying to pass a null value as an object reference
Error
error external to our application
Ex. memory error, stack overflow error
Solution?
identify source like infinite recursion or problem with JVM itself
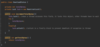
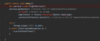
What are checked exceptions?
Exceptions we should anticipate and recover from vs. runtime terminating program
Exceptions we as developers should anticipate and handle
Exceptions forced to handle by Java compiler
Checked at compile time by java compiler (red underline)
Ex. Java compiler knows constructor will throw an exception if file is not present, must handle this edge case

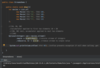
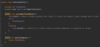
What are unchecked exceptions (run time exceptions)?
Programming errors
not checked during compile time by Java Compiler
NullPointerException - due to trying to pass a null value as an object reference
ArithmeticException - attempt to divide by zero
IllegalArgumentException - argument passed to method not accepted
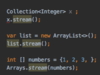
IndexOutOfBoundsException - access an array, list, string invalid index
IllegalStateExceptions - call a method, object not in correct state
Solve?
Automated Testing, lots of testing

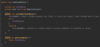
What are errors?
errors resulting from problems external to our application
Ex.
StackOverFlowError
OutOfMemoryError
Source?
Infinite looping, JVM issues
Solve?
Let application crash, identify error source

What is the stack trace?
Shows the methods that have been called (in reverse order) that resulted in an exception
Why?
Useful in solving problems & identifiying sources of exceptions, errors

What can throw an exception?
A method can throw an exception
or cause of chain of exceptions
What is the exceptions hierarchy?
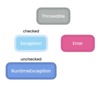
Classes that represent different types of exceptions
Top of Hierarchy:
Throwable Class - defines common characteristics for all exceptions and errors like an error message and stack trace
Next Level:
Exception Class - parent class for all checked and unchecked errors, if not RunTimeException it’s a checked error
Error Class - + all children classes represent errors external to our application errors
Below Exception Class:
RunTimeException Class - unchecked exceptions

What will Java run time compiler do when a method throws an exception?
Look for an exception handler
If the method doesn’t have a method to handle the exception, will look at other methods
if none are present, Java Run Time will terminate the program and deliver exception message
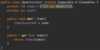
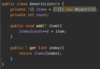
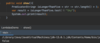
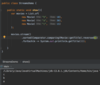
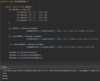
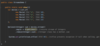
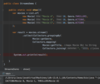
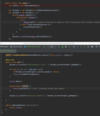
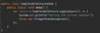
E What is the proper way to handled checked exceptions?
Catch exceptions using try-catch blocks!
How can we use IntelliJ to generate a catch for a checked error?
Option + enter
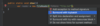
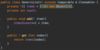
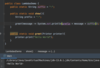
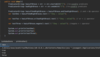
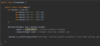
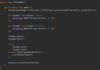
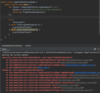
How do we catch multiple types of exceptions?
Multiple catch blocks
each catch block targets a specific exception
if method throws an exception
catch block will catch exception and handle it
Sometimes order matters!
Why?
A parent object might get called first, resulting in absence of polymorphism (child object not getting called)
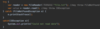
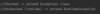
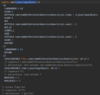
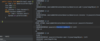
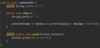
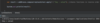
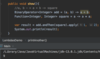
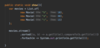
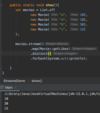
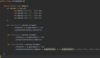
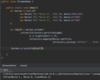
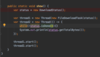
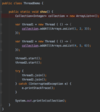
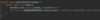
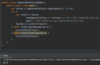
How can we refactor these exceptions?
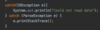
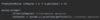
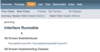
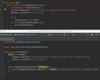
Combine the two exceptions using a vertical bar
block will catch exceptions of type IOException or ParseException and handle them the same
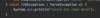
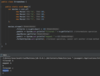
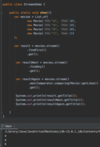
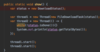
What is the finally block?
Comes after catch statement
always gets excuted (whether there is an exception or not)
allows us to release external resouces
Release:
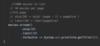
File Handles - reader.close ( );
Network connections
Database connections
Why?
If we don’t release these ext. resources other methods may not be able to access them!

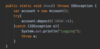
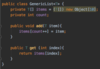
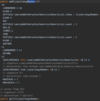
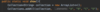
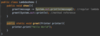
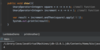
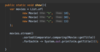
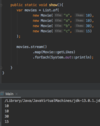
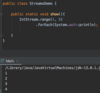
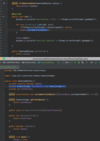
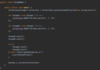
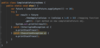
What is a better way to release resources (than finally block)?

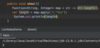
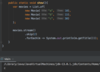
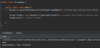
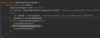
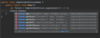
use try-with-resources statement
a try statement with one or more resources
We don’t need to explicitly close resources
Syntax?
initialize external resources after try statement before block using ( )
Why?
JavaCompiler will automatically create finally block (at runtime, under the hood, close resources)
But?
Objects initialized in try-with-resource statement must implement the auto-closeable interface
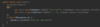
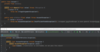
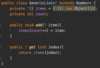
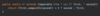
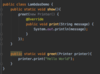
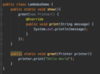
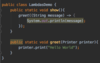
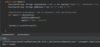
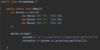
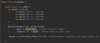
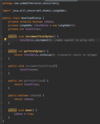
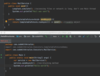
How can we throw an exception?
Use the throw keyword!
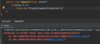
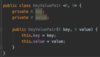
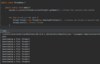
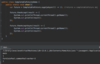
What is defensive programming?
validating an argument, throwing an exception if outside of valid range
Why?
stopping code from running is better than letting a serious problem occur later in our application
When?
if an error could occur that causes problems with the rest of our code
Do?
Throw an exception to prevent rest of code from running if an error occurs
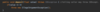
When is it better to use defensive programming?
- When building a library for others to use
- When recieving data from external sources outside of application
Why?
Defensive programming makes your code verbose
If building an application, methods should trust each other, don’t need to pollute your code with tons of data validation
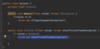
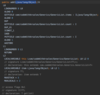
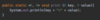
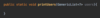
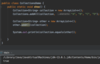
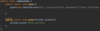
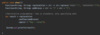
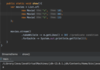
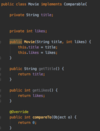
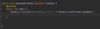
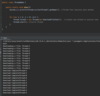
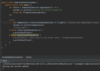
How do we specify that our method may throw an exception so that the receiving class can handle this exception?
Add the throws keyword after parameter declaration
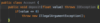
details represent API of this method