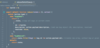
Redux Flashcards
(140 cards)
What will we learn?
everything we need to know to build real, complex apps with Redux
work on a real bug tracking app with a node backend
by end of course, know and understand Redux inside/out

What is Redux?

A state management library for Javascript applications
doesn’t care what library we use for UI development
instead of scattering app state across UI
store state in a single JS object (store)
single source of truth
like a “database” for front end
components get state from store
data is updated in a single place
can see how data changed, why, when and where it came from

Why do we need redux (state managment)?

complex UI, need to keep in sync
data updates from backend request, user interaction, etc. changes must be reflected immediately

What are the pro’s of Redux?
debugging
transparent state changes
can reload state, view actions and see UI changes
cache/preserve page state
entire app state available on client in JS object (store)
don’t have to reload data from server
centralized state
data is available in one place, accessible by all parts of UI

When is redux NOT right for my project?

must consider constraints and problem domain
A real software engineer is an active problem solver
not every application requires Redux
DON’T USE
if load data and display statically (not changing)
if it’s a tight budget
if the UI is very simple
**it will be complex and slow you downl
What is functional programming?

Redux is built on top of functional programming
A good background is critical to building redux apps
One of the programming paradigms
Each paradigm has rules for how to structure code to solve problems
invented in 1950s
decomposing a problem into small, re-usable functions
can compose functions to build complex pipelines
Pros
can run in parrallel
exploit multiple cores
Benefits:
more concise
easier to debug
easier to test
more scalable

Why are functions first class citizens in Javascript?
can treat them like any other variables
assign them as variables
pass them as arguments
return them from other functions
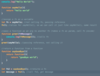
What are higher order functions?
a function that…
takes a function as an argument
returns a function
both!
Why?
instead of working on strings, numbers or booleans
it goes higher to operates on functions
What is the problem with this approach?
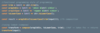
expression is read right to left
trim, make lowercase, wrap in div
so many parenthesis
Soln?
What is currying?
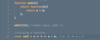
Solves this problem:
functional pipeline
function in line requires two parameters (fns)
only have one fn as parameter
How?
allows us to take a fn with N arguments
convert it to an fn with 1 argument
What?
instead of separating args with commas “,”
separate with ( )
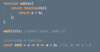
What is the challenge with this code?

wrap function expects two arguments
if we pass type as argument
pipeline will throw an error
Why?
it requires a function as argument, not string
Soln?
currying

What are pure functions?

a function that given the same args, produces the same result

NOT:
random values
current date/time
global state
Why?
These change
Redux?
reducers must be pure
other fns don’t have to be
What are the benefits of pure functions?

Self documenting
everything a fn needs is clearly identified in parameter signature
easier to test
no global state
concurrency
because not using global state
can run in parallel
cacheable
can store result in cache and use in future
useful in programs with intensive computations
if we know certain computations produce same results
can optimize by storing in a cache
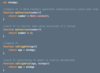
What is immutability?
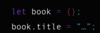
Goes hand in hand with pure functions

once we create an object, cannot be changed
must take a copy and change that copy
Ex. Strings are immutable, create copy, original string not affected
Objects and arrays can be modified directly, not immutable
Does “const” prevent mutability?
No
it prevents re-assignment
common misconception
Ex. cannot re-assign book to another object
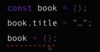
What are the benefits of immutability?
Predicatable apps
if we call a fn, pass an obj
obj won’t get changed, no suprises down road
Fast change detection
React needs to know when changed
creating a new obj, stored in memory
React compares objects by references
this is fast operation
in contrast, without immutability
React has to compare all properties in two objects to see it’s changed
slow operation
Concurrency
can run in parallel
not going to affect something that affects system as a whole

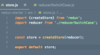
What is the problem with this code?
Spread operator does a shallow copy
nested objects are copied by reference (not value)
Ex. Both person2 and person2copy have the same reference to “address” in memory (not copied by value) copied by reference
Soln?
Do a deep copy
set a new nested object using spread operator

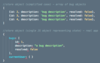
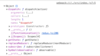
How do we copy an array and insert a number at a specific location?

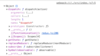
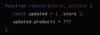
How do we update an array using immutability?
Hint:.map ( ) method

How do we enforce immutability?

By default, Javascript doesn’t do this
Why?
It’s a multi paradigm language
it doesn’t enforce immutability without libraries
Soln?
Libraries that enforce real immutability
Different people love different tools
Immutable.js (by Facebook)
Immer (becoming trendy, Mosh loves it)
What is immutable.js?
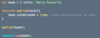
Hint: npm i immutable
a library by Facebook
provides a bunch of immutable data structures
*Mosh prefer’s another library
How?
instead of a plan JS object
use one of the datastructures from this library
Problems?
have to learn a new API
cannot access obj properties with . or [] notation
have to use .get( ) method
integration with other libraries
hard to integrate with other libraries that expect plain JS objects
have to call .toJS( ) method to convert to plain JS objects
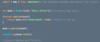
What is Immer?
Hint: Immutability library (npm i immer)
almost as popular as immutable.js
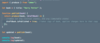
Pros
writing code as if mutating objects but actually not
better than using spread operator (get’s nasty with nested objs)
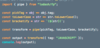
Write code to solve this?
Hint: function composition

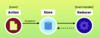
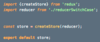
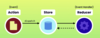
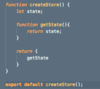
What are the three building blocks in Redux applications?
Store
single JS Object that includes application state
Actions
plain JS Objects that represent what happened
aka events (what happened)
Reducers
one or more functions responsible for updating a slice of Store (single JS object)
aka event handlers or processors
pure functions, don’t mutate arguments, no side effects