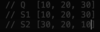Linear Data Structures Flashcards
(152 cards)
What is Big O notation?
Big O is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function where the argument tends toward a particular value or infinity.
What is Big-O?
Helps us determine if an algorithm is scale-able or not

When do we use Big O notation?
Describe the performance of an algorithm
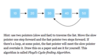
What are the five common Big-O curves?
O( 1 ) - constant time
O ( n ) - linear time
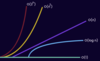
What are the five common time complexity curves?

How does linear big - O grow?
Linearly and in direct proportion to the size of the input
What is O(n^2)?
Quadratic.

Nested loops
How does the logarithmic curve behave?
It slows down as the input size grows
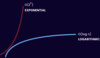
What is exponential time complexity?
The exponential curve grows faster as the input grows.
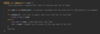
What is the shortcut to run JVM in debug?
Control + D
When would we have a quadratic Big-O value?
When we use nested loops that each performs an iteration over the entire set of values.
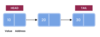
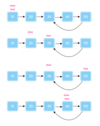
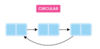
What are the linear data structures?
- Arrays
- Linked Lists
- Stacks
- Queues
- Hash Tables
What are arrays?
Reference type
fixed-length data structure.
Values are indexed sequentially in memory.
Optimal for looking up values by their index.

What can we use arrays for?
We use arrays to store lists of values like strings, objects or anything.
These items are stored sequentially in memory.
Can store strings, objects, numbers or anything.
What are the pro’s of arrays?
Looking up the index is very fast
why?
item index lookup doesn’t involve loops or complex data access operations.
What are the disadvantages of arrays?
They’re fixed length.
Not good for storing values that need to be added or deleted frequently.
Adding or deleting an item requires copying old array into a new array with a cost of O(n).
How do we keep track of the number of items in our array?
Using a private variable “count”
increment count for each new item
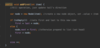
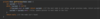
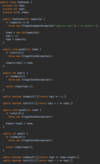
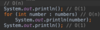
How do we implement resizeIfRequire ( ) in our addItem method of our array class?
Create a new array x 2 size
copy items into new array
O ( n ) operation!

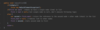
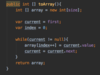
How do we implement the removeAt ( ) method in our array class?
Shift items left
Copy items from [index + 1] into [index]

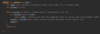
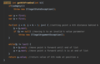
How can we implement the print ( ) method in our custom array class?
Use a for loop to iterate over each index
+ print on console
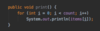
How can we implement the max ( ) method in our Array class?
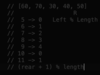
What is run time complexity?
O(n):
have to iterate over the entire array to find the largest number.
This number may be at the end of the array (worst case scenario).
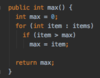
How to implement the insertAt ( ) method in our Array class?
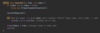
How to implement the reverse ( ) method in our Array class?
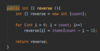
How to implement the intersect ( ) method in our Array class?
Foreach loop + nested if loop