Basics_Java Flashcards
(185 cards)
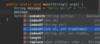
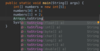
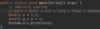
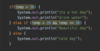
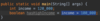
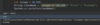
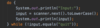
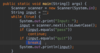
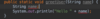
Where do we put parameters for a function?
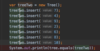
we use parameters to pass values to function
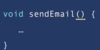
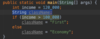
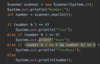
Where do we put the methods for our functions?
Inside the curly braces.
In Java the curly brace is on line with function name and return type
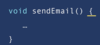
what is a good function (method name)?
clearly identifies the purpose of the function
camelCase notation
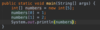
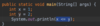
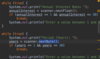
What is a function?
A block of code that performs a task
Think of buttons on a remote
In Java, functions are the smallest building blocks
Ex. functions to validate user info, convert weight to kgs
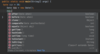
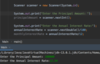
What is a package?
A concept for grouping related classes.
We will have hundreds or thousands of classes.
We should organize these classes into packages.
Java creates a namespace for our classes:
com.namespace
*every class we create in our program will belong to this package
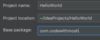
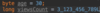
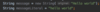
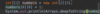
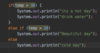
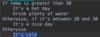
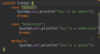
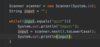
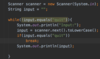
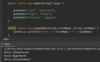
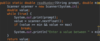
Where do we specify a return type?
A function is a block of code that performs some task.
We specify the return type before the name.
Some functions don’t return anything.
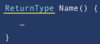
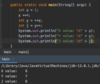
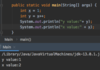
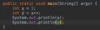
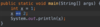
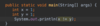
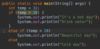
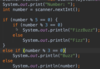
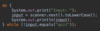
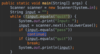
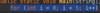
Where is the entry point into our program?
Every Java program must have one function.
The main function is executed first.

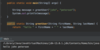
What is a class?
A container for related functions.
We use classes to organize our code.
Ex. The supermarket has related products in different “classes” or sections.
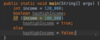
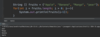
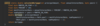
What class must every Java program have?
Every program in Java has a main class that contains the main function.

What is a method?
A method is a function that is part of a class
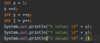
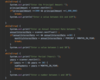
What is an access modifier?
A special keyword that determines if other classes and methods can access these classes and methods.
Private
Public
What is the naming convention for classes and methods?

What are the two steps involved in running a Java program?

How do we get byte code?
Java Compiler changes our source code into byte code
Who developed Java?
At Sun Microsystems.
Sun Microsystems was later acquired by Oracle in 2010.
It was originally called Oak named after the tree outside Goslings office.

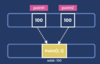
Where can our Java byte code run?
Java byte code is platform-independent
It can run on Linux, mac, windows or any operating systems that have a Java Run-Time Environment
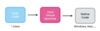
What is java byte code?
The instruction set for the Java Virtual Machine
Assembled code is runnable on a CPU with a specific instruction set, while bytecode can be executed in a virtual machine (such as the Java runtime) on any CPU that can run the VM. Assembly code is (represents) the native code for the processor you are programming.

What is a Java Run Time Environment?
The Java Runtime environment has a component called Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
JVM translates our byte code into the native executable language for various platforms (Mac, Windows, Linux)
What is byte code?

What does the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) perform?
Converts our Java Byte code into the native code for the operating system we are using like a mac, windows or linux operating system.
This makes applications portable.
Can execute on Linux, Mac or any other operating systems that have a Java Run-Time Environment.
Who owns Java?
Oracle
Oracle Corporation is the current owner of the official implementation of the Java SE platform, following their acquisition of Sun Microsystems on January 27, 2010.
How many editions are there of Java?
Four Editions for different types of applications
SE - all the libraries all Java developers must learn
EE - provides additional libraries for building fault-tolerant multi distributed systems
ME - libraries specific for mobile phones
Java Card - for smart cards

How many worldwide developers does Java have?
9 million developers world wide

How many mobile phones run Java?
3 billion mobile phones currently run Java