OOP_Javascript Flashcards
(78 cards)
Why is this course important?
(Hint: Immense career impact)
Why?
A lot of developers write JavaScript applications without properly understanding the inner workings of JavaScript.
Don’t be one of these!
Get a solid foundation of the inner workings of JavaScript
It’s an immense help to your career

What are technical interviewers looking for?
(Hint: Object Oriented Programming)
Understanding of Object Oriented Programming
Why?
makes a candidate stand out!
What are popular interview questions?
Pillars of Object Oriented Programming:
Encapsulation
Abstraction
Inheritance
Polymorphism

What does this course teach?
OOP principles + how to implement in Javascript!
What is procedural programming?

A style of programming
bunch of variables that contain data
a number of functions that act on the data
As program grows, you have functions all over the place
You will copy and paste functions all over the place
If you change one function the others break
Soln?
Object Oriented Programming

What are the benefits of Object Oriented Programming?
- Reduce complexity, increase reusability - group related variables and functions together to reduce complexity + increase reusability in applications and programs (encapsulation)
- Hide complexity - hide complexities from consumers, reducing complexity of applications, increasing speed and safety of programs (abstraction)
- Reduce redundant code - reduce redundant code by allowing objects to inherit code from a parent (Inheritance)
- Eliminate switch cases - eliminate switch cases by allowing objects to override inherited methods (Polymorphism)

What is object-oriented programming?

a very popular style of programming
It’s a model or pattern of programming
centered around objects rather than functions
OOP is not a programming language or tool!
It’s a style or model of programming
many frameworks are built using object oriented programming
HLL support OOP -
C#, Java, Python and Javascript
What problem does object oriented programming solve?

Spagetti code -
procedures (functions) all interconnected
change one function, other’s break
too much interconnection between functions
Soln?
combine functions and data into units (objects)

What problem does encapsulation solve?
(Hint: too much interconnectedness)
Spagetti code
Hint: too much interconnectedness

What problem does abstraction solve?
This helps us reduce impact of change
simpler interface for objects
Making changes to the private method doesn’t cause issues in rest of the applications code because these changes don’t leak to the outside

What problem does inheritance solve?
(Hint: reduce redundant code)
It helps us eliminate redundant code
We can define properties and methods once in a generic object
other objects inherit these properties and methods
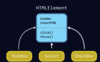
What are the two types of inheritance?
Classical vs. prototypical
Javascript doesn’t have classes and inheritance is implemented using prototypical inheritance!
What problem does polymorphism solve?
(Hint: elminate if/else and switch/case statements)
allows us to get rid of switch/case statements
Example:
We can implement a render method in each object
render method will behave differently depending on type of object referencing

What are the topics covered in objects?
Javascript is all about objects:
Creating objects
factoring constructors
adding, removing properties
private properties
getters/setters

How do we define an object?
use let or const
Why?
ES6 scope
don’t use var (scope issues)
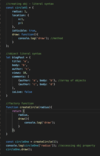
What is object literal syntax?
(Hint: avoid for objects with methods)
Don’t use with objects that have behavior
Why?
If changes to a function is required, have to update multiple spots of code

What is an object in Javascript?
collection of key-value pairs
we can have key and value as a function
we can have a key and value as an object
This object has three “members”
If a member is a function we refer to it as a “method.”
the other members are “properties”

What is an object property?
(Hint: object member)
A member of an object that holds a value is called a property

What is an object method?
A function defined inside an object
called a method and is used to define some logic

How can we access an object’s members?
(Hint: dot or bracket)
access values and methods
using the dot notation
Bracket notation

In what ways can we define objects?
using object literals (simple) curly braces
using factories, using constructors
When do we say an object has “behavior”?
If an object has more than one method we say that object has “behavior”
Why is object literal syntax not a good way to create and duplicate an object with behavior?

(Hint: copy code to duplicate)
You will have to copy the exact code to duplicate the object
If there is a bug in the function, you’ll have to change in multiple places
It acts like procedural programming

When is object literal syntax not a problem?
if the object doesn’t have behavior or methods
Only has variables and values