Thorax 2 (Cardiovascular System) - part 1 Flashcards
(221 cards)
Vaugly, what does the mediastinum contain?
Contents of the thorax other than the lungs and their covering pleurae
What are the sections of the mediastinum?
Superior
Inferior (further divided)
What is the inferior mediastinum further divided into?
Anterior
Middle
Posterior
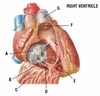
What is A?

Pericardial cavity
What is B?

Pleural cavity
What is C?

Pleura
What is D?

Spinal cord
What is E?

Right lung
What is F?

Mediastinum
What is G?

Heart
What is H?

Left lung
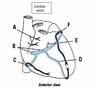
What is A?

Superior mediastinum
What is B?

Inferior mediastinum
What is C?

Sternal angle
What bone forms the anterior border of the mediastinum?
Manubrium
What vertebrae form the posterior border of the superior mediastinum?
T1 - T4
What plane seperates the superior from the inferior mediastinum?
Transverse
What are some structures found in the superior mediastinum?
Arteries (aortic arch, brachiocephalic artery, left common carotid artery, left subclavian artery)
Veins (brachiocephalic vein, superior vena cava)
Nerves (vagus nerve, phrenic nerve)
Trachea
Oesophagus
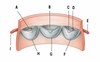
Picture is the inferior mediastinum, what is A?

Middle mediastinum
Picture is the inferior mediastinum, what is B?

Posterior mediastinum
Picture is the inferior mediastinum, what is C?

Anterior mediastinum
Where in the mediastinum is the thymus found?
Anterior
Where in the mediastinum is the heart, pericardium and great vessels found?
Middle
Where in the mediastinum is the descending aorta found?
Posterior