Thorax 1 (Respiratory System) - part 1 Flashcards
What does the thoracic wall enclose?
Left and right pleural cavities (containing the lungs)
Mediastinum
What is the function of the thoracic wall?
Protect the contents inside the pleural and percardial cavities
Permits movement associated with respiration
What is the thoracic wall composed of laterally?
Ribs 1-12
What is the thoracic wall composed of anteriorly?
Sternum
What is the thoracic wall composed of posteriorly?
Vertebrae 1-12
What bones articulate with the manybrium at its superolateral angle?
First ribs
What is the name given to the joint between the superolateral angle of the manubrium and the first ribs?
Sternocostal joint
What is the name given to the notch formed by the superior border of the manubrium?
Jugular notch
At what vertebrae level is the xiphoid process (xiphisternum) located?
T10
At what vertebrae level is the sternomanubrial joint located?
T4
What component part of the sternum do the facets for the 2nd costal cartilage articulate?
Manubrium sterno joint
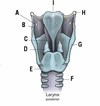
What is A?

Jugular notch
What is B?

Clavicular notch
What is C?

Manubrium
What is D?

Sternal angle
What is E?

Body
What is F?

Xiphoid process
What ribs are known as typical ribs?
Ribs 3-9
What are ribs 3-9 known as?
Typical ribs
Where does the head of the typical rib articulate?
T2 and
Where does the tubercle of a rib articulate?
Transerve process of vertebrae
What structures lie in the costal grove of a rib?
Intervostal vein, artery and nerve
What ribs are the true ribs?
Ribs 1-7
What ribs are false ribs?
Ribs 8-10