STEEPLECHASE - Special Senses EAR Flashcards

Otodectes cynotis

Otodectes cynotis

Demodex canis

Demodex canis / cati

Sarcoptes scabiei var. canis - mites found on deep skin scrapes - burrowing mite

Sarcoptes scabiei var. canis - mites found on deep skin scrapes - burrowing mite



Foreign body

Acute atopy

Acute atopy

Chronic atopy

Chronic atopy

Cutaneous adverse food reaction (CAFR)

Contact hypersensitivity - erythema often seen dorsally and ventrally to external acoustic meatus (where medication is common in contact w/ skin of ear)



Keratinisation disorders - endocrine disease (hypothyroidism, hyperadrenocorticism, sex hormone dermatoses); sebaceous adenitis; primary idiopathic seborrhoea





Feline ceruminous cystomatosis




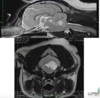
Feline nasopharyngeal (inflammatory) polyp - non-neoplastic feline ear mass

Feline nasopharyngeal (inflammatory) polyp - non-neoplastic feline ear mass












Canine juvenile sterile granulomatous dermatitis and lymphadenitis (puppy strangles)

Canine juvenile sterile granulomatous dermatitis and lymphadenitis (puppy strangles)



Multifocal lesion of erythema, plaques + patches of alopecia due to dermatophytosis

Erythematous macules due to canine distemper virus

Aural haematoma - dog bites, pruritus, blunt trauma

Aural haematoma


Squamous cell carcinoma - due to actinic dermatitis

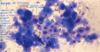
Bacterial cocci


Streptococcus spp.

Biofilm

Biofilm cytology

Malassezia dermatitis



Roughened mucosa due to Malassezia dermatitis



Progressive pathologic change


Progressive pathologic change - epithelial folds = fibrosis + creates niche for microbes

Progressive pathologic change










Equine aural plaques (ear pinna papilloma) - perpetuating factor of otitis externa/media

Normal hairy ear canal of labradoodle - confirmation predisposition to otitis

Aural haematoma - serosanguinous fluid formed haemorrhage distends the pinna and creates a cavity between the skin and cartilage of pinna

External ear

Ear canal - covered by squamous epithelium