Ocular Histopathology Flashcards

Normal eye histo




What is a common feature of corneal oedema?
- Dehydrated cornea - reduced corneal stromal clefting
- Superficial injuries to the cornea can cause corneal oedema - generally more limited to the area of injury e.g. ulceration








What is the most predisposing factor of glaucoma?
Increased intraocular pressure
What is goniodysgenesis? (2)
- Cocker Spaniels predisposed (autosomal-recessive condition)
- Associated with defective drainage angle (pectinate ligament never rarified to the point that it should be in development)
- Cause of 1^y glaucoma













Lens equator - one side more rounded than the other










What is the process by which the outflow of aqueous humour gets occluded? (3)
- Inflammation - obscures ciliary cleft
- Neovascular membranes proliferate in response to uveitis (particularly in dog)
- Uveitis leads to secondary glaucoma through synechiae (iris adheres to cornea (anterior)/lens (posterior)


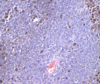
Diffuse iris melanoma















Small lymphocytes + plasma cells (lymphocytic + plasmacytic)

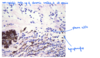
What are the three different patterns of ocular inflammation? (3)
- Uveitis - inflammatory cells limited to uvea
- Endophthalmitis - retina (inner layers) + chambers get involved with exudates
- Panophthalmitis - when all the layers of the eye including tunic and orbit are affected

Endophthalmitis



What is a pathognomic lesion of equine recurrent uveitis?
Amyloid + rod-shaped eosinophilic inclusions




What is is a lesion of equine/large animal glaucoma?
Atrophy of corpora nigra (iris modification)







What is a morgagnian globule?
Lesion of cataracts - when lens fibres swell + become more distinct + individualised. If identified with a nucleus = bladder cells


What are two main mechanisms of glaucoma-related corneal oedema and
how do they differ?
- Corneal endothelial injury – generally diffuse
- Exposure keratitis – usually focal/regional
What is the MAJOR site of injury in glaucoma-related vision loss?
Optic nerve head/lamina cribrosa/inner retina
Explain how glaucoma and lens luxation are interrelated
Buphthalmia can cause luxation; lens location can cause secondary glaucoma
What is the most common predisposing factor for glaucoma?
Elevated intraocular pressure/obstruction of aqueous outflow
Name two sites where aqueous outflow can be impeded
Ciliary cleft; pupil margin (pupil block/iris bombé)
Name the most common primary feline intraocular neoplasm
Diffuse iris melanoma
Name two mechanisms by which ocular neoplasia can cause glaucoma
Physical obstruction of aqueous drainage
How do patterns of glaucomatous retinal damage differ between cats and
dogs?
- Cats: limited to inner retinal atrophy;
- Dogs: Advanced/full-thickness atrophy ventral
What is the most reliable indicator of chronicity of corneal disease?
Neovascularisation
Name two mechanisms by which ocular neoplasia can cause lens luxation
- Secondary glaucoma/buphthalmia
- Physical displacement/disruption of zonules
What is the most common cause of equine glaucoma?
Equine recurrent uveitis
How does IOP (intraocular pressure) typically change in uveitis? Glaucoma?
Uveitis: Low; Glaucoma: Elevated
What are the two most common mechanisms by which uveitis leads to
glaucoma?
Neovascular membranes/synechiae; occlusion of outflow by cells/matrix
How are uveitis and cataract interrelated?
Cataract can cause lens-induced uveitis; uveitis can cause cataract
Differentiate the distributions of: uveitis; endophthalmitis; panophthalmitis
- Just uvea;
- Uveitis + retina/chambers;
- All layers of the eye (including fibrous/orbit)


