Morphology Flashcards
(32 cards)
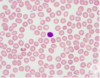
What cell is this

Megakaryocyte
What abnormality is shown here and what can casue it?

Hypersegmented neutrophil
Caused by Vit. B12/folate deficiency
What does this blood film show
Normal RBCs
What abnormality is shown here, and what are the causes

Spherocytes
Caused by RBC membrane defects, such as Herdeitary spherocytosis and haemolysis
What is the difference between normal RBCs and spherocytes?
Spherocytes don’t have the central pallor, they are deformed and have a smaller diameter
They can also lead to the destruction of the spleen
Spherocytes and microcytic RBCs both have a decreased cell diameter, but what is the main difference between the two other than the buggered shape?
Microcyitic RBCs still have their central pallor
(unlike spherocytes)
What abnormality is this

Microcytic RBCs
What is the proper name for Teardrop cells on a blood film?
Dacrocytes
What abnormality is shown hear and what is a potential cause

Tear-drop RBCs (dacrocytes)
Potential cause -> myleofibrosis
What abnormality is shown here and what are some potential causes

Cabot Ring
Potentially causes: Vit. B12 deficiency & myleofibrosis
What 2 abnormalites are shown here, and what is a potential cause

Target cells and Spur cells
Potential casue -> microcytic anaemia due to Crohns
What is the proper name for spur cells?
(mon the spurs ehhhhhh)
Acanthocytes
What abnormality is shown here

Spur cells (acanthocytes)
What is the proper term for sickle cells
Drepanocytes
What abnormality is shown here

Sickle cells
(drepanocytes)
What is another name for RBC fragments?
Schistocytes

What are Helmet cells a type of?
Schistocytes
What abnormality is shown here and what is a potential cause

Schistocytes (inlcuding helmet cells)
Causes -> Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
What happens to the platlet count if there are lots of schisocytes (like in TTP)?
It falsely increases
Because automated cell counters think that the schistocytes look like platlets LOL
What abnromality is shown here, what is the name of the cells and what is the likley cause?
Oxidative haemolysis
Shows ‘Blister’ cells
Potential cause is G6PD deficiency
What abnormality is shown here

RBC Agglutination
What cell is this on a blood film, and what condition is present

Myeloblasts
Myeloid malignancy (cause there’s Auer Rods)
What is a potential sign of myeloid leukaemias on myeloblasts?
Auer Rods

What cell is this

Lymphocyte


