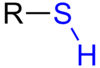Molecular Representation Flashcards
(46 cards)
What type of functional group is this?

Alcohol
A carbon atom become an anion when it has how many bonds?
3 bonds and a lone pair
What type of functional group is this?

Carboxylic Acid
What type of funtional group is this ?

Alkyene
What functional group is this?

Amide
What type of functional group is this?

Aldehyde
What type of functional group is this?

Keytone
Lead compound
The known compound that leads the way to other similar compounds
What type of functional group is this ?

Ester
Auxophore
Refers to the rests of the compound that arent responsible for the analgesic activity
Nitrogen atoms are cation when they have how many bonds?
4 bonds
What are the five patterns to recognize when drawing resonance structures?
- Lone pair on the outside (allylic lone pair)
- Lone pair near a positive charge that is on the outside (An allylic postive charge)
- Lone pair (negative charge) near a positive charge
- A double bond connected to an electromegative atom
- Aromatic (Ring) alternating double bonds
Allylic Position
The outer atoms that are directly connected to those carbons
Pharmacphore
Portions of the compound responsible for the analgesic activity
Haworth Projection
Used for Cyclic Compounds
Nitrogen atoms are anions when they have how many bonds?
2 bonds and 2 lone pairs
Localized lone pairs
Lone Pairs that don’t participate in resonance
Delocalization
Spread of a charge & is a stablizing factor
What type of functional group is this?

Ether
What type of functional group is this ?

Alkyl Halide
What type of functional group is this?

Acyl Halide
Halogens are cations when they have how many bonds?
2 bonds & 2 lone pairs
What type of functional group is this?

Aromatic
Halogens are anions when they have how many bonds?
no bonds all lone pairs