Lab 7: Tissues & Quiz Prep Flashcards
(137 cards)
4 tissue types
- Epithelial
- Connective
- Muscular
- Nervous

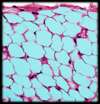
Adipocyte
(Adipose Connective Tissue)

Basal body
(Pseudostratified columnar epithelial)
Basal cellular components
- Cell membrane (or plasma membrane)
- Surrounds the cell and separates it from its surroundings
- Nucleus
- Contains the genetic material (DNA)
- Cytoplasm
- Includes everything inside the cell except for the nucleus
- Goblet cell
- Specialized type of columnar epithelial that makes mucus

Basement membrane
(Simple columnar epithelial - ciliated)

Basement membrane
(Simple columnar epithelial - nonciliated)

Basement membrane
(Stratified columnar epithelium)



Capillary
(Adipose Connective Tissue)

Capillary
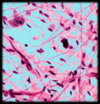
(Areolar connective tissue)

Capillary
(Transitional epithelium)

Cement line of osteon
(Compact bone)

Central canal of osteon
(Compact bone)

Chondroblast in lacuna
(Elastic cartilage)

Chondrocyte in lacuna
(Hyaline cartilage)

Cilia
(Pseudostratified columnar epithelial)

Cilia on simple columnar epithelia
(Simple columnar epithelial - ciliated)

Collagen fiber
(Fibrocartilage)

Collagen fiber
(Areolar connective tissue)

Collagen fiber
(Dense irregular connective tissue)

Collagen fiber
(Dense regular connective tissue)
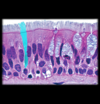
Columnar epithelial
(Pseudostratified columnar epithelial)

Columnar epithelial
(Simple columnar epithelial - ciliated)

Columnar epithelial
(Simple columnar epithelial - nonciliated)