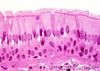
Histology/Epithelial Tissue Flashcards
tissue
a group of cells and their extracellular matrix specialized to perform the same function

extracellular matrix
environment around cells
4 main types of tissue
-epithelial -connective -nervous -muscle/contractile
epithelial tissue
-covers all structured surfaces -lines all hollow chambers and organs -makes up all glands
connective tissue
-provides support, structure, and transport
nervous tissue
provides a flow of information through electrical signaling
muscle/contractile tissue
provides movement
major functions of epithelial tissue
-protection -absorption -filtration -secrete/excrete -provide sensation
protection of epithelial tissue
protects from internal and external environment
Absorption of epithelial tissue
ex: nutrients from food in digestive system
filtration of epithelial tissue
-turns metabolic waste into urine -water retainment, etc.
secrete/excrete of epithelial tissue
-excretes CO2 -secretes oxygen, hormones, etc.
provide sensation (epithelial tissue)
ex: cones in retina
characteristics of epithelial tissue
-location -orientation -alignment of cells -avascular -regenerate cells
lumen
space
apical
faces empty space

basal
forms base of tissue

basement membrane
provides attatchement to other tissues

alignment of cells in epithelial tissue
-tightly packed -no extracellular matrix -allows for more permeability
permeability
-“gate keepers” -controls what gets in/out
avascular
no direct blood flow
avascular in epithelial tissue
epithelial tissue relies of adjacent tissue for blood floq
cells regenerate in epithelial tissue
-specific to epithelial tissue -very limited in all other tissues
apical adaptation
-microvilli -cilia