Gait and limp - Physiology Flashcards
(31 cards)
Describe the components of the somatic motor (simple) reflex arc
- Stimulation of receptors e.g., externoreceptors (sight, sound, vision, taste, smell, pain, touch, thermal) or proprioreceptors (muscle and joint position)
- A sensory (afferent) neurone carries information to the CNS from recepors
- A motor efferent neuron transmits information from the CNS or spinal cord via single motor nerve myelinated and fast conducting to the periphery e.g., neurmsucular junction to skeletal muscle

List 3 functions of the motor control system
- Posture and balance
- Goal-directed movements
- Communication
Describe the 3 classes of movemement
- Voluntary
- Complex actions
- Purposeful goal directed
- Learned
- Involuntary/reflexes
* Rapid, stereotypes (knee jerk, eye blink0 - Rythmic motor patterns
- Combines voluntary and reflexive acts (chewing, walkng, running)
- Initiation and termination voluntary but once initiated it is repetitive and reflexive
Describe the organisation of the spinal cord in reference to motor control
- Primary sensory afferent neurons enter spinal cord via dorsal root (and terminate within laminae I to IV)
- This meets with interneurones within the dorsal and ventral region in anterior horn and synapse in the α-motoneurons
- α-motoneurons’ cell bodies lie in clumps within ventral horn of the spinal cord (lower motor neurone)
- Each motor neuron in ventral activates a motor unit (an α motor neuron and all of the skeletal muscle fibers that its axon supplies)
- Motor neruons project their axons into the periphery to innervate skeletal and smooth muscles that mediate voluntary and involuntary reflexes.
- Some axon branch back into cord and synapse with interneurons called Renshaw cells (recurrent or feedback inhibition)
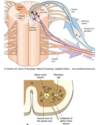
a) Some axon branch back into cord and synapse with interneurons called Renshaw cells (recurrent or feedback inhibition). Describe the role of renshaw cells
b) Describe the role of renshaw cells in strychine poisoning
a) Suppress weakly firing motor neurons and dampening strong firing ones - modulate firing rate/muscle activity - produces econmical movemement
b) Strychnine poisoniig disables renshaw cell inhibiton which leads to convulsion
a) List the sensory fiber types from largest diameter to smallest diameter
b) What is the relationship between the diameter and conduction of speed.
c) What is the fast and the slowest sensory neurone?
a) Largest diameter to smallest: Aα, Aβ, Aδ, C
b) As the fiber diameter decreases the conduction velocity decreases
c) Aα fastest and C slowest

Fill in the empty boxes


a) List the motor fiber types from largest diameter to smallest diameter
b) What is the relationhsip between the diameter and conduction of speed.
c) What is the fast and the slowest motor neurone?
a) From largest diameter to smallest diameter: Aα, Aγ
b) As the diameter decreases the conduction velocity decreases
c) Fastest is Aα and slowest is Aγ

Fill in the boxes


List the sensory and motor neurone fibers
Sensory: Aα, Aβ, Aδ, C
Motor: Aα, Aγ
Label the structures of the muscle fiber

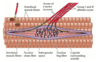
Describe how muscle spindles detect and respond to changes in muscle length.
Muscle spindles respond to changes in muscle length because they lie in parallel with the extrafusal fibers and therefore will also be stretched or shortened along with the extrafusal fibers.
Because intrafusal fibers (like all muscle fibers), display spring-like properties, a change in their length will change the tension that they are under, and this change is sensed by mechanoreceptors of the Ia and II spindle afferents.
Myotatic (knee jerk) reflex is an example of a monosynaptic reflex. Describe how this occurs
- Tap of patella tendon stretches quadriceps muscle
- This stimulates dynamic nuclear bag receptors of muscle spindle
- Increase in rate of firing of group of Iα afferent leads to contraction of quadriceps muscle
- Iα fibers also stimulate inhibitory interneurons which inhibit antagonist (flexor) muscle of knee joint

How is the myotatic (knee jerk) reflex lost?
Reflex is lost if lower lumbar dorsal root of spinal cord is damaged
a) What is the role of the golgi tendon organ
b) Describe how it is activated?
c) Describe how it is innervated
a) Detects the force in tendon
b) Activated by muscle stretch and contraction
- Information on static
- Rate of change in length
- Force generated
c) Sensory innervation - Group Ib afferent - wrapped about bundles of collagen fibers in the tendon of the muscle
a) What is the role of the inverse myotatic (golgi tendon) reflex
b) Describe how it wokrs
a) Contributes to maintenance of posture
b)
- During maintained posture (e.g., standing), quadriceps muscle will start to fatigue
- Force in patellar tendon will decline, thus activity in afferent Ib fibers will decline
- Normal inhibiton of motor neurons supplying quadriceps will be removed
- Muscle will contract more strongly, so increasing force in patellar tendon
Descrbe the role of the withdrawal reflex and crossed extensor reflex
- Withdrawal reflex - protective reflex from damaging stimuli
- Crossed extensor reflex - stimulation of withdrawal reflex, frequently elicits extension of the contralateral limb 250ms later - helps maintain posture and balance

a) Where is the central pattern generation (CPG) for locomotion
b) What is its role?
c) What is it modulated by?
d) What is it thought to be initiated by?
a) Spinal cord
b) Neural networks in the spinal cord, referred to as “central pattern generators” (CPGs), are capable of producing rhythmic movements, such as swimming, walking, and hopping, even when isolated from the brain and sensory inputs - Therefore capable of autonmous signals.
c) Modulated by proprioception input
d) Thought to be initiated by mesencephalic locomotor region - output through reticular nulei and reticulospinal tracts
List the 5 components of the motor cortex
- Primary motor cortex (M1)
- Four premotor cortical arears:
- Supplementary motor area (SMA)
- Cingulate gyrus
- Ventral premotor cortex
- Dorsal premotor cortex

List the structures of the basal ganglia/nuclei
- Neostriatum: Caudate nucleus and putamen
- Globulus pallidus
- Subthalamic nucleus
- Substantia nigra
Label the structures of the basal ganglia/nuclei


a) List the 3 pathways of basal ganglia/nuclei
b) Describe the roles of the pathways of basal ganglia/nuclei
a) Hyperdirect pathway, direct pathway and indirect pathway
b)
- The pathways are responsible for initiation and termination of movement/motor programmes
- Gives an inhibitory effect on the globus pallidus. This stops the inhibiton of the thalamus and allows thalamocortical neurons to initiate the movement

Describe the role of the cerebellum
Adjusts motor responses by comparing the intended output with sensory signals and to update movement commands if they deviate from the intended trajectory
What role does the cerebrocerebellum input from the cerbral cortex have?
Role in movement planning and initiation of movement




