GA: Ear Flashcards
What are the 3 general divisions of the ear?
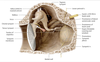
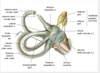
Inner ear: auricle (pinna) + external acoustic meatus (ear canal)
Middle ear: Tympanic cavity + epitympanic recess (ossicles: malleus, incus, stapes + chorda tympani N. + tympanic plexus)
Internal Ear: Vestibulocochlear organ (hearing _ balance)

Parts of Auricle


What is the blood supply for the auricle (& pinna)?
Posterior Auricular + Superficial Temporal A.’s
(from ECA)
What is the innervation for the auricle?
Great auricular N.
Auriculotemporal N.
Vagus N.
Facial N.
What causes an auricular hematoma?
Trauma to ear –> causes blood to build up between perichondrium + cartilage
If not drained, fibrous tissue can form and this can cause califlower ear
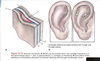
What does the external acoustic meatus consist of?
lateral 1/3 = cartilage
medical 1/3 = bone
Which way do you pull an ear during an exam?
Posterior, Superior, and slightly lateral
What is otitis externa?
“swimmers ear”
Infection of external acoustic meatus
Risk factors: excessive moisture (pool), trauma (cleaning), anything the covers ear canal (earphones)

What is the purpose of the tympanic membrane?
It separates the external acoustic meatus from the middle ear.
Reflects cone of light
Where are the incus + malleus heads found?
In the epitympanic recess of
Which “portion” is the cone of light in?
Anterior and Inferior
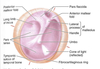
What is otitis media?

Infection of the middle ear
Causes swelling of tympanic membrane and can block pharyngotympanic tube (eustacian tube)

Describe the steps taken in treatment of chronic middle ear infections (i.e. myringotomy and tympanostomy).
You would place a tympanostomy tube.
myringotomy –> incision to open eardrum
tympanostomy –> tube placed for continual drainage

What is the middle ear cavity roof boundry?
Tegmen tympani bone
Separates tympanic cavity from middle cranial fossa (temporal bone & brain)
Infection here can cause meningtitis
What is the middle ear cavity floor boundry?
bone
Separates tympanic cavity from the bulb of the internal jugular V.