Flashcards - Cardiology
Fetal Circulation
Umbilical Vein –> ductus venosus –> IVC –> RA –> foramen ovale –> LA –> LV –> Aorta –> umbilical arteries –> placenta
AV/SA node circulation
RCA
Aortic receptor nerve
Vagus
Cushings triad
HTN, bradycardia, bradypnea
allantois/urachus
median umbilical ligament
ductus arteriosus
ligamentum arteriosum
ductus venosus
ligamentum venosum
notochord
nucleus polposus
umbilical arteries
medial umbilical ligaments
umbilical vein
ligamentum teres hepatis
Fetal hemoglobin
alpha2-gamma2
holosystolic high pitched blowing
MR/TR
crescendo decrescendo murmur
aortic stenosis
holosystolic harsh murmur
VSD
late systelic crescendo murmur
MVP
early diastolic high pitched blowing murmur
AR
rumbling late diastolic with opening snap murmur
MS
continuous machine like murmur
PDA
ANP/BNP
cGMP - vasodilation, decreased Na resorption, dilates afferent renal aterioles, contricts efferent arterioles
dilated cardiomyopathy causes
alcohol, wet beriberi, coxsackie, cocaine, chgas, doxorubicin, hemochromatosis, carcoidosis, peripartum
restrictive cardiomyopathy causes
sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, loffler syndrome, hemochromatosis
a1 receptor
Gq - vascular smooth muscle contraction, pupillary muscle contraction, intestinal/bladder sphincter muscle contraction
a2 receptor
Gi - decreased sympathetic - decreased insulin, lipolysis, ciliary production of aqueous humor, increased platelet aggregation
b1 receptor
Gs - increased HR, contractility, renin, lipolusis
b2 receptor
Gs - vasodilation, bronchodilation, increase lipolysis, insulin, decreased uterine tone, ciliary muscle
ANP
cGMP stimulator
Class 1A
increase AP duration, effective refractory period, QT interval Quinidine, Procainamide, Disoprymide
Class 1B
decrease AP duration, preferentially affects resting cells Lidocaine, mexiletine
Class 1C
prolongs ERP in AV node, decreases slope of Phase 0 only Flecainide, propafenone
Class 2
b-blockers
Class 3
Potassium channel blockers - amiodarone, ibutilide, dofetilide, sotalol
Class 4
calcium channel blockers - verapamil, diltiazem
dihydropyidines
act on smooth-muscle - amlodipine, clevidipine, nicardipine, nifedipine, nimondipine
non-dihydropyridines
act on heart - diltiazem, verapamil
CCB toxicity
AV block, edema, flushing, hyperPRL, gingival hyperplasia
Hydralazine
increases cGMP - smooth muscle relaxer
Fenoldopam
Dopamine D1 receptor agonist - coronary, peripheral, renal, splanchnic vasodilation
Digoxin toxicity treatment
normalize K, magnesium, anti-dig Ab
fibrates + statins
myopathy
angiosarcoma
malignant - associated with polyvinyl chloride, arsenic
Cystic Hygroma
cavernous lymphangioma of neck, associated with Turners
Bacillary angiomatosis
benign capillary skin papules of Bartonella henselae, found in AIDS patients, looks similar to Kaposi’s but has neutrophils
Glomus tumor
painful red-blue tumor under fingernail, from smooth muscle of glomus
long QT causes
antiarrythmics (Class IA, ibutilide, dofetilide, sotolol), antibiotics, anticychotics, antidepressants, antiemetics
Romano-Ward syndrome
AD - long QT syndrome - only cardiac
Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome
AR - long QT syndrome - +sensorineural deafness
Brugada syndrome
AD - asian males, pseudo-right bundle branch block + ST elevations in V1-V3, increased sudden cardiac death
Einsenmenger syndrome
Uncorrected L-to-R shunt (ASD, VSD, PDA) - pulmonary hypertension, RVH, clubbing, polycythemia, cyanosis
22q11 associated cardiac malformation
Tetralogy of Fallot, truncus ateriosus
Williams syndrome associated cardiac malformation
Supravalvular aortic stenosis
hyperplastic arteriosclerosis (onion skin)
malignant hypertension
hyaline arteriolosclerosis
diabetes
ateriolonephrosclerosis
glomerular scarring from diabetes
Monkeberg
calcification of medium arteries, not clinically significant
JONES criteria
for acute rheumatic fever - joints, carditis, nodules, erythema marginatum, sydenham chorea
bacterial M protein
rheumatic fever, molecular mimicry
Down syndrome cardiac defects
endocardial cushion defects (ASD, AV regurg)
DiGeorge cardiac defects
ToF
Friedreich’s ataxia cardiac defects
HOCM
Marfan cardiac defects
cystic medial necrosis of AOrta
Tuberous sclerosis cardiac defects
cardiac rhabdomyomas
Turners cardiac defects
Coarctation of aorta
polymyalgia rheumatica
temporal (giant cell) arteritis
Polyarteritis Nodosa
multiple organs except lung, associated with HBsAg, fibrinoid necrosis/strings on a bead
Buerger disease
associated with smoking, ulcers on feet/fingers, raynauds phenomenon
Wegeners/GPA
nasopharynx, lungs, kidney - c-ANCA - cyclophosphamide
microscopic polyangitis
GPA, but no nasopharynx and no granulomas - p-ANCA
Churg-Strauss
eosinophilia, hx of asthma - p-ANCA
HSP
IgA deposition/nephropathy s/p URI

Class IA - Quinidine, Procainamide, Disopyramide

Class IB - Lidocaine, MexileTine

Class IC - Flecainide, Propafenone

Class II - Metoprolol, propranolol, esmolol, atenolol, timolol, carvedilol.

class III - K+ blockers - Amiodarone, Ibutilide, Dofetilide, Sotalol
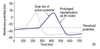
class IV - CCBs - non-dihydropyrimidines - Verapamil, diltiazem
transmural inflammation of arterial wall with fibrinoid necrosis
polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) - associated with hepatitis B
His/Purkinje Fiber AP ion movement

packemaker ion movement

Variant (prinzmetal) angina treatment
coronary artery spasms - CCBs, nitrates
Kussmaul sign
increased JVP on inspiration - seen in constrictive pericarditis, restrictive cardiomyopathies, right A/V tumors
Korotkoff sounds
audible during expiration with blood cuff, audible all phases w/ cuff release. due to pericardial disease/tampanade, restrictive cardiomyopathy.
plump macrophages with abundant cytoplasm and central round/ovoid nuclei with central slender chromatin ribbons
Anitschow cells - sign of acute rheumatic carditis, when multinucleated are Aschoff giant cells


