Exam 1: T-cell Types and Functions Flashcards
(29 cards)
Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs)
Characteristics
- Recognize Ag in class I MHC-restricted manner
- Kills infected cells or those expressing “altered-self” Ag
- Can make IL-2, IFN-α, and TNF-α
- Major role in defense against viral infections and malignant cells
- Causes damage during autoimmune diseases or transplant rejection
Precursor CTLs
- Recently activated naïve CD8+ T-cells cannot kill due to insufficient granules
- Needs time to mature before effector functions active
CD8+ T-cell
Activation
-
TH - cell independent
- APC (Dendritic cells) ⇒ licensed/active APC
- MHC-I+Peptide and costimulation signal (B7-1 or B7-2)
- APC signal must be strong enough to stimulate CD8+ T-cells to produce IL-2
-
TH - cell dependent (most effective)
- TH cell with same TCR specificity helps
- Upregulates co-stimulatory molecules on APC’s (B7-1)
- Produces IL-2 which helps activate CTL
CTL
Killing Mechanism
Selective serial killers.
Requires cell-cell contact.
Cells die by apoptotic death to prevent lysis and release of the pathogen.
-
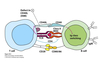
Fas/FasL pathway
- Ca2+ dependent
- “Extrinsic” path
- Recruitment of “death domain” containing molecules
- Caspase 8 ⇒ ⊕ caspase 3
-
Performin/granzyme pathway
- Pore can form on plasma membrane or endosomes
- Ca2+ independent
- “Intrinsic” path
- Apaf-1 and procaspase-9 ⇒ ⊕ caspase 9
- ⊕ effector caspase 3 by cleavage
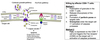
Apoptosis
CTLs kill via apoptosis.
Neutrophils, macrophages, and complement induce a necrotic death.

NK Cells
- Large lymphocytes that participate in the innate immune response
- Defense against viruses and malignant cells
-
Activated by:
- IgG leading to ADCC
- Lack of class I MHC on target cell
-
Kills via:
- Perforin and granzyme
- Fas:FasL
- Secretes IFN-γ and TNF-α
-
Stimulated by:
-
IFN-α / IFN-β
- From virus-infected cells
- Favors development of cytotoxic effector function
-
IL-12
- Made by macrophages
- Favors IFN-γ production by NK cells (and Th1 cells)
- Acts as a positive feedback loop further activating macrophages
-
IFN-α / IFN-β
Viral Infection
Timeline
-
Early during a viral infection:
- IFN-α, IFN-β, and IL-12 ⇒ NK cell activation
-
NK Cells
- Produces most of the IFN-γ
- Provides most of the cytotoxicity against infected cells
-
Later on in the infection:
-
Cytotoxic CD8+ T-cells specific for the virus generated
- Becomes the main IFN-γ producers
- Becomes the main anti-viral cytotoxic cell
-
Cytotoxic CD8+ T-cells specific for the virus generated
Missing Self Model
- Normal cells present a ligand for the activating and inhibitory receptors (MHC I) on NK cells
- When viruses infect cells, some may inhibit MHC class I expression to evade CTLs
- Makes them prime target for elimination by NK cells
- NK cells recognize and kill infected and tumor cells by absence of MHC class I
TH Cell
Cytokine Function
Helps to select which immune effector mechanisms engaged:
- CD8+ cell proliferation and activation
- Macrophage activation
- NK cell activation
- B cell proliferation, activation, and isotype switching
TH Cell
Class Determination
- Initial local cytokine environment during T-cell activation and development
- Self-promoting regulation
- Cross-regulation between classes

TH1 Cell
Induction
- Functions through T-bet transcription factor
- ⊕ by IL-12 and IFN-γ
- ⊗ by IL-10

TH2 Cell
Induction
- Functions through GATA3 transcription factor
- ⊕ by IL-4
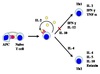
TH Cell
Self-Promoting Regulation
-
TH1 cells
- IFN-γ ⇒ ⊕ T-Bet ⇒ ↑ IFN-γ
-
TH2 cells
- IL-4 ⇒ ⊕ GATA-3 ⇒ ↑ IL-4 & IL-5

TH Cell Class
Cross-Regulation
-
TH2 cells produce:
- IL-10 ⇒ ⊗ TH1 pathway
- IL-4 ⇒ down-regulates T-bet ⇒ inhibits IFN-γ effects
-
TH1 cells produce:
- IFN-γ ⇒ down-regulates GATA-3 ⇒ ⊗ TH2 pathway

Model of TH Cell
Cytokine Secretion

Comparison of TH Cell Profiles

TH1 Functions
Recognizes bacterial peptides:MHC II ⇒ activates macrophages.

TH2 Functions
Recognizes antigenic peptide:MHC II ⇒ activates B-cells.

TH17 Cells
- Proinflammatory cells
- Generated early in immune response when mature microbe-activated dendritic cells make high levels of IL-23, IL-6, and TGF-β which stimulate naive CD4+ T-cells
- Down-regulated to IFN-γ or IL-4 (Th1 or Th2 response)
- Produces IL-17 and IL-6:
- ⊕ neutrophil recruitment
- ⊕ fibroblast/epithelial cell cytokine production
- Role in bacterial and fungal defense
Treg Cell
Function
- Role in inducing peripheral tolerance
- Prevents inappropriate immune responses against self-Ag or commensal microorgansims
- Down regulation of immune responses
Treg Cell
Induction
- In absence of infection
- Dendritic cells make TGF-β >> IL-6
- Continue to present self & environmental Ag
- Continue to deliver Ag to lymph nodes
- Naive CD4+ T-cell stimulated by a dendritic cell producing high TGF-β but no other cytokines involved in TH cell differentiation
- Leads to expression of transcription factor FoxP3
- Results in Treg cell generation
- Deficiency in FoxP3 causes absence of Treg ⇒ IPEX disease
Treg Cell
Mechanism
Expresses both CD4 and CD25 (α-subunit of IL-2R).
Produces IL-10 and TGF-β.
Treg cells inactivate traditional T-cells by:
-
Cytokine deprivation
- CD25 binds IL-2 with low affinity ⇒ no activation
- Generation of inhibitory cytokines ⇒ TGF-β
- Inhibiting APCs
- Cytotoxicity
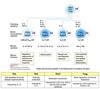
Th Cell Class Summary
Thymic Indepedent B-cell Activation
- T-cell indepedent Ag
- Ex. polysaccharides, lipopolysaccharides, and proteoglycans with repetitive epitopes
- Able to activate naive and/or mature B cells without activating T cells
-
Without T-cell help:
- ↓ isotype switching
- ↓ somatic mutation
- ↓ memory development
- Age dependent