Exam 1: Inflammation & Hematopoiesis Flashcards
Inflammation
Characteristics
Redness
Swelling
Heat
Pain
Loss of function
Factors Stimulating
Inflammation
Endogenous
- Tissue necrosis
- Bone fracture
- Urate crystals
Exogenous
- Mechanical injury (cut)
- Physical injury (burn)
- Chemical injury (caustic)
- Foreign bodies
- Immunocological process
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Immune complex deposition
- Biological injury
- Microorganism infection
Identifying Characteristics
of
Inflammatory Pathways
- Mechanism of induction
- Time course
- Types of cellular infiltrates
- Kind of inflammatory cells that enter the tissue
Inflammatory
Enzyme Cascades
- Coagulation system
- Fibrinolytic system
- Complement cascade
- Kinin system
- Lipid inflammatory mediators
- Arachidonic derivatives
Complement Role
in
Inflammatory Response
- Destruction of target membranes via MAC complex
-
Phagocyte recruitment
- C5a > C3a
- Activates vascular endothelium
- Chemoattractants
- C5a > C3a >>> C4a
- Anaphylatoxins ⇒ induce mast cell degranulation
- ↑ histamine and arachidonic acid products
- Induces smooth muscle contraction
- ↑ vascular permability
- Anaphylatoxins ⇒ induce mast cell degranulation
- C5a > C3a
-
Opsonization
- C3b and C4b on target binds complement receptors (CRs) on phagocytes
-
Promotes clearance of immune complexes
- CR1 on RBC’s
- Reticuloendothelial system
Proinflammatory Cytokines
IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α ⇒ proinflammatory
IL-8 ⇒ chemokine
- Contribute to the inflammatory response prior to or in the absence of adaptive immune response
- Sources:
- Resident macrophages
- 1st phagocytic cells to encounter pathogen in the tissue
- Damaged epithelial & endothelial cells
- Inflammatory macrophages
- Recruited to the site of infection/injury
- Resident macrophages
- Production induced by:
- PAMPs
- DAMPs
- Tissue damage/stress
Proinflammatory Mediators
- Products of arachidonic pathway
- Products of clotting cascade
- Products of fibronolytic cascade
- Pro-inflammatory cytokines
Kinin-Kallikrein
System
- Hormonal system consisting of blood protein
-
Influences:
- Inflammation
- BP control
- Coagulation
- Pain
-
Important mediators
-
Kallidin → Bradykinin ⇒ vasodilators with broad effects
- Formed in response to injury
- Plasmin ⇒ protease that degrades many blood plasma proteins, including fibrin clots
-
Kallidin → Bradykinin ⇒ vasodilators with broad effects

Acute Inflammation
Local Effects of Proinflammatory Mediators
-
Induce changes in blood flow and leukocyte flow patterns
- Larger vessels ⇒ slower flow
- Easier diapedesis
- Causes redness & warmth
- Larger vessels ⇒ slower flow
- Increase vascular permeability
-
Activates vascular endothelium
- ↑ expression of cellular adhesion molecules
- Aids in extravasation of WBC’s
- Creates a chemotactic gradient
- ↑ microbicidal activity of phagocytes
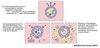
Acute Inflammation
Systemic Actions
“Acute-phase response”
Attributed to high concentrations of IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α.
Typically induced by bacterial infections.
-
Fever
- Caused by endogenous pyrogens
- IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, prostaglandins
- ∆ hypothalamus ⇒ ↑ temperature set point
- Mechanism used by body to kill bacteria
- Caused by endogenous pyrogens
-
Leukocytosis
- ↑ WBCs in blood
- Infection with extracellular bacteria ⇒ ↑ IL-1 & IL-6 ⇒ neutrophilia
- ↑ band cells in peripheral blood
- Left-shift
- ↑ band cells in peripheral blood
- ↑ production of acute-phase proteins
- Stimulated by IL-6, IL-1, TNF-α
- Includes MBP and CRP
- Liver can ↑ production 1,000x
- Onset 12-24 hours
- Responsible for increase ESR
- Due to ↑ protein concentration in peripheral blood
-
Mobilization of energy from fat and muscle stores
- Triggered by TNF-α
-
Blood vessel occlusion
- Triggered by TNF-α
- ∆ endothelial cell surface molecules ⇒ blood clotting in small blood vessels
- Local ⇒ prevent microbial migration
- Systemic ⇒ Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
- Failure to profuse tissues/organs ⇒ organ failure/death
- Consumption of clotting factors ⇒ bruising, failure to clot, bleeding
-
Endotoxic shock / septicemic shock
- Caused by massive release of TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6
- Induced by bacterial products
- Ex. LPS from Gram ⊖ bacteria
- Results in life threatening consequences
- Fever
- Circulatory collapse
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- Consumption of clotting proteins
- Hemorrhagic necrosis
- Multi-organ failure

Neutrophil
Characteristics
“PMNs”
- Hallmark of acute inflammation
- Most common WBC in peripheral blood
- Generated in bone marrow in a manner responsive to demand
- Band cells ⇒ immature peripheral blood neutrophils
- Circulates in blood for 1-2 days
-
Mobilized into tissues within hours of stimulus
- Short-lived in tissues (half-life ~ 7 hours)
- Die via necrosis at site of infection forming pus
- Undergoes apoptosis in absence of infection
- Kill via oxygen-dependent & independent mechamisms
- Sources/reserves
- # 1 - blood
- # 2 - bone marrow
- # 3 - hematopoiesis
WBC Recruitment
- Activation of vascular endothelium
- Adherence
-
Diapedesis
- Movement of the cell between endothelial cell junctions into tissues
-
Chemotaxis
- Movement of the cell towards the “threat”
- Travels along a chemotactic gradient
- C5a or IL-8
Activation of Vascular Endothelium
-
Infection or tissue damage ⇒ release of pro-inflammatory mediators
- Bradykinin, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, C5a
-
Mediators activate the endothelium
- ↑ expression of P & E - selectins
- ↑ expression of ICAM
Neutrophil Recruitment
A model for leukocyte recruitment:
-
Rolling/tethering
- P-selectin and E-selectin on activated endothelium binds the sialyl Lewisx expressing carbohydrate ligand PSGL-1 on neutrophils (& most other WBC’s)
- Produces a “weak adhesion”
- Promotes tethering/rolling along the endothelium causing WBC to dramatically slow down
-
Sampling & chemoattractant-mediated activation (stimulation)
- Rolling allows WBC to “sample” its environment for chemoattractants
- Ex. C5a, IL-8, histamine
- Chemoattractants “activate” WBC
- Integrin (LFA-1) on neutrophil undergoes a conformational change
- ↑ integrin affinity for ligand (ICAM) ⇒ allows firm adhesion
- Specific chemoattractant recruitments specific cell type
- IL-8 ⇒ neutrophils
- IL-5 ⇒ eosinophils
- Rolling allows WBC to “sample” its environment for chemoattractants
-
Firm adhesion & pavementing
-
LFA-1 : ICAM interaction causes cell to:
- Stop rolling
- Firmly adhere
- Flatten
-
LFA-1 : ICAM interaction causes cell to:
-
Diapedesis
- Neutrophil moves between endothelial cells into tissue
-
Chemotaxis
- Follows IL-8 chemotatic gradient to site

Secondary Capture
Another method of neutrophil recruitment:
- PSGL-1 on free flowing neutrophils can bind to P-selectins presented on adherent platelets
- L-selectin on free flowing neutrophils can interact with PSGL-1 presented by adherent leukocytes or leukocyte-derived fragments
Neutrophil Receptors
Neutrophils express > 40 receptor types:
-
Fc receptors (FcR)
- Bind the Fc region of an Ab
- Complement receptors (CR1 and CR3)
-
Collectin Receptors
- Allows cell to bind acute phase proteins
- MBP & CRP
- Allows cell to bind acute phase proteins
-
PRR
- Examples:
- Toll-like receptors
- Scavenger receptors
- Binds to PAMPs on pathogens
- Can induce phagocytosis
- Examples:
Fc and complement receptors act in synergy.

Neutrophils & Macrophages
Methods of Killing
-
Oxygen-dependent mechanisms
- ROI, ROS
-
Oxygen-independent mechanisms
- Defensins
- Cathepsin G
- Lysozyme
- Bactericidal permeability increasing (BPI) proteins
- Nitric oxide and RNIs
Use multiple strategies hoping that bacteria is not resistant.
Needs to be able to work in an environment which is oxygen poor such as an injury site.
Inflammation Resolution
-
Monocytes begin to accumulate several hours after arrival of PMNs
- Attracted by cytokines, complement components, and DAMPs
-
Recruited monocytes become activated macrophages
- Mop-up bacteria, dead PMNs, and tissue cells
- Macrophages and T-cells release:
-
Anti-inflammatory cytokines
- Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)
-
IL-10
- Inhibit M1 macrophage activation and cytokine production
- Alter/inhibit certain T-cell functions
-
Anti-inflammatory cytokines
-
Drainage of interstitial fluid (extravascular edema)
- Drains via lymphatics
- Promotes movement of APCs and Ag to naive/memory lymphocytes in secondary lymphoid organs
- Promotes adaptive immune response
- Facilitates lymphocyte activation
-
Lymphocytes recruitment
- ↑ trafficking of antigen-activated lymphocytes
- CD4+/CD8+ effector T-cells
- B-cells
- ↑ trafficking of antigen-activated lymphocytes
-
Tissue repair and scar formation
- M2 Macrophages
- Fibrosis
- Granuloma formation
- M2 Macrophages
IL-10
- Produced by M2 macrophages and T-cells
-
Suppresses M1 macrophage function
- ↓ cytokine production
- ↓ respiratory burst
- Alters adaptive CD4+ T-cell response
Transforming growth factor β
(TGF-β)
Produced by M2 macrophages and T-cells:
- Limits inflammatory response
- Inhibits many components of innate and adaptive immunity
- Promotes accumulation of M2 macrophages
- Promotes accumulation and proliferation of fibroblasts and deposition of ECM
- Alters cell cycle to stop lymphocyte proliferation
Acute Inflammation
Summary
- Event
- Tissue damage and/or macrophage activation
-
Release of proinflammatory mediators
- ∆ blood flow
- ↑ vascular permeability
- Activation of vascular endothelium
-
Recruitment and killing by neutrophils
- Adherence
- Rolling/tethering by P & E Selectin : PSGL-1
- Sampling and activation by chemoattractants
- Firm adhesion by LFA-1:ICAM interactions
- Attachment of neutrophil to pathogen
- Phagocytosis
- Killing by oxygen dependent & independent mechanisms
- Adherence
-
Normal resolution and repair
- Recruitment of macrophages and lymphocytes
- Drainage of insterstitial fluid
- Adaptive immune response
- Repair of tissue and scar formation
Chronic Inflammation
- Occurs when the offending material or pathogen cannot be destroyed and cleared by neutrophils or macrophages
- Macrophage accumulation and activation are the hallmarks of chronic inflammation
- Prolonged Ag stimulation leads to continued arrival of new macrophages and T cells
- Chronic inflammation can lead to fibrosis or granuloma formation which can alter tissue function
- Histiocyte epitheliod cells
- Giant cells
Fibrosis
- Thought to occur when macrophages and TH cells interact together over many weeks to years.
- TH cells make IFN-γ that activate macrophages
- Macrophages stimulate TH cells
- Macrophages synthesize growth factors that:
- promote inflammation
- stimulate fibroblast proliferation
- cause excessive collagen deposition
- If offending material cannot be removed or is toxic to macrophages, macrophage enzymes released into the tissues leading to excessive damage
Granulomas
- If macrophage unable to clear pathogen then T-cells release IFN-γ which stimulate macrophage to become epitheloid cell or giant cell
- T-cells form a barrier around the outside of macrophages to form granuloma.
- If T-cell function drops then granulomas fail and pathogens may re-emerge.






