Exam 1: T Cell Activation and Effector Functions Flashcards
(16 cards)
Antigen Sources
-
Tissue antigens
- Immature APCs phagocytize Ag
- Langerhans cells
- Resident macrophages
- Carries Ag via lymph to lymph node
- Immature APCs phagocytize Ag
-
Intersitial fluid antigens
- Draining fluids carry Ag to lymph node
- Ag activates APCs with LN
- Dendritic cells
- Macrophages
- B-cells

Professional APCs
-
Macrophages
- Exogenous Ag from phagocytosis
-
B cells
- Ag binds BCR
- Exogenous Ag from Clathrin-coated vesicle endocytosis
- Very homologous Ag due to BCR specificity
-
Dendritic cells
- Most potent APC for naïve T cells
- Bone marrow derived
- Found in virtually all tissues
- Langerhan cells ⇒ immature dendritic cell in skin
- Constantly phagocytize until “danger signal” occurs
- Skin damage or infection
- PAMPs or DAMPS : PRR
- Travels tissue ⇒ lymph node
- Maturation ⇒ endocytose or pinocytose but no longer phagocytic
- ↑ MHC I and II expression
- ↑ B7 expression

Naïve T-cell
Circulation
- Enter the lymph node via peripheral blood through high endothelial venules (HEVs)
- Search for MHC+peptide match
- Exit via lymphatics → circulation → another LN
- Maximizes opportunity for Ag+MHC recognition
Naïve T-cells
Lymph Node Recruitment
-
Rolling and sampling
-
L-selectins (T-cell) : CD34 (HEV)
- L-selectin only expressed on naive T-cells
- Targets them to LN
-
L-selectins (T-cell) : CD34 (HEV)
-
Stimulation
- Chemokine ⇒ conformational ∆ of LFA-1 ⇒ ↑ affinity for ICAM-1
-
Firm attachment and pavementing
- LFA-1 (T-cells) : ICAM-1 (HEV)
- Diapedesis

Naïve T-cell
Activation
- Naïve T cells “sample” MHC+peptide
- Low affinity interactions via adhesion molecules
- LFA-1 : ICAM-1
- TCR engagement ⇒ ↑ binding affinity of adhesion molecules
-
Requires two signals for activation:
- TCR engagement ⇒ TCR : peptide+self-MHC
- Co-stimulatory signal ⇒ CD28 (T-cell) : B7 (APC)
- Only TCR engagement ⇒ anergy
- Facilitates extra-thymic self & tumor tolerance

T-Cell
Signaling
Common to CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cells:
- TCR engagement ⇒ clustering of TCRs, CD4/CD8, CD28, and other cell surface receptors
- Transphosphorylation of Lck and Fyn (protein tyrosine kinases)
- Activated Lck & Fyn phosphorylate ITAMS on CD3 and ζ-chains
- ZAP70 (Zeta-associated protein tyrosine kinase-70) docks via ITAM-℗
- Lck phosphorylates ZAP70 ⇒ activation
-
ZAP 70 phosphorylates numerous proteins
- Phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ)
- Guanine nucleotide exchange facors (GEFs)
-
PKCγ and GEFs initiate cascades ⇒ transcription factors
- NFAT, NF𝛋B, and AP-1
- Cyclosporin and FK506 inhibit calcinerin ⇒ ⊗ transcription factors ⇒ immunosuppresion
-
Induces transcription of many genes
-
IL-2 and IL-2 receptor α-chain
- Required for T cell proliferation and differentiation
- T-cells say IL-2, I love you
-
IL-2 and IL-2 receptor α-chain

T-Cell
Proliferation
Clonal proliferation ⇒ T cell response
Mechanism of antigen-specific T cell amplification:
-
IL-2 Receptor is a trimeric protein (α, β, and γ)
- β and γ chains constitutively expressed
- α-chain expressed on activated T-cells only
- Trimeric complex needed for IL-2 binding and signaling at physiological levels
- IL-2 : IL-2R ⇒ T cell proliferation

Toxic Shock Syndrome
- Superantigen activates polycolonal T-cells in Ag-independent manner
- Causes a cytokine storm ⇒ massive release of IL-2

Effector and Memory T-Cell
Activation
Effector and memory T cells ony requires TCR enagement for activation.
TCR : peptide+self-MHC
Still prefers CD28 : B7 interaction also.
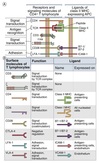
Effector T-cell
Peripheral Tissue Targeting
Effector T-cells no longer express L-selectin
Other molecules target it to site of infection/inflammation:
-
Rolling and sampling
- Mediated by P and E-selectins on activated endothelium
-
Stimulation
- Chemokine ⇒ conformation ∆ of LFA-1 and VLA-4 ⇒ ↑ affinity for ligands
-
Firm attachment
- LFA-1 (T-cell) : ICAM1 (endothelium)
- VLA-4 (T-cell) : VCAM-1 (endothelium)
- Diapedesis
- Chemotaxis

Effector TH Cell
Functions
“CD4+ T-cells”
- Primarily involved in cytokine production
- Effects:
- CD8+ cell proliferation → defense against viruses & malignant cells
- Macrophage activation → intracellular bacteria
- NK cell stimulation → viruses, malignant cells
- B cell proliferation / isotype switching → viruses (extracellular stages), bacteria (extracellular), helminthic parasites

Effector TC Cell
Functions
“CD8+ T-cells”
- Kills virally infected, malignant, or foreign cells
- Up to 1,000 cells per NK cell via apoptotis

T-cell Lifecycle
Summary

Immune Response
Down Regulation
T-cell activation and proliferation dependent on antigen stimulation:
-
Clearance of threat
- Loss of T-cell activation signals
- Stop IL-2 and IL-2R synthesis
- Loss of survival factors
- Death by apoptosis
-
Down-modulatory cytokines
-
TGF-β made by regulatory T-cells
- Inhibits the immune response
-
TGF-β made by regulatory T-cells
Within 1-2 weeks of clearance, the only remaining component of the immune response is a pool of memory cells.
Immunological Memory
Memory ⇒ provide protective immunity so subsequent exposure results in an absent, subclinical, or mild infection.
Mechanisms:
- Pre-existence of a clonally expanded population
-
Memory cell fuctionally different
-
Faster response
- Naïve cells take 4-5 days
- Memory cells take 1-2 days
-
Better response
- T-cells ⇒ more complex cytokine profile
- B-cells
- Different isotypes: IgG, IgA
- Higher affinity
- Greater Ab titers
- Lower Ag titer required for activation
-
Faster response
Life of a T-cell
Summary
- Naïve T-cells wait in the periphery for specific Ag stimulation
- Naïve T-cells can recirculate for ~ 1 year
- Actual fate of these cells unknown
- Unclear if body produces subclinical Ag levels so memory cells stimulated and life extended



