EKG III and IV (Exam 3) Flashcards
Which kind of sinus dysrhythmia is this:
Rhythm: regular
Rate: <60 bpm
P wave: one for every QRS, nl in size/shape/direction
QRS complex: normal (<0.12sec)
Sinus bradycardia

Junctional rhythms originate in the
a. SA node
b. AV node
c. Bundle of Kent
d. Bundle of His
AV node! If you chose bundle of kent you owe me a crisp $20 bill.
You are looking at an EKG from left to right and it’s going normal, normal, normal, normal, wide QRS followed by a T wave in opposite direction of QRS, normal, normal, normal…
what the heck was that one weird thing in the middle?

Premature ventricular contraction (PVC). They can be unifocal or appear in groupings (bigeminy: every other complex, or trigeminy: every third complex)
Sorry, it’s hard to explain without seeing a picture! Hopefully not too confusing…. see slides 55-58
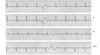
“Saw-tooth” pattern should make you think of……

Atrial flutter!
- Single irritable atrial foci initiates beat rapidly (rate around 300bpm)
- Results in “flutter waves” preceding QRS complex, hence the saw-tooth pattern

Define sinoatrial/sinus arrest
SA node fails to initiate a beat
- Rhythm: irregular
- Rate: changing
- P waves: one for every QRS, however a pause (>2 sec) occurs and a new rhythm is then started
- PR interval: nl (0.12-0.20 sec)
- QRS complex: nl (<0.12 sec)
*Often concerning

What is the normal duration of the QRS complex?
0.12 sec or less
Define sinus arrhythmia
SA node initiates beat but at varying intervals:
- Rhythm: irregular (R to R varies and P to P varies)
- Rate: varies
- P waves: one for every QRS, nl in size/shape/direction
- PR interval: nl (0.12-0.20 sec)
- QRS complex: nl (<0.12 sec)
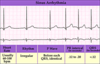
What’s going on with multifocal atrial tachycardia and how do you identify it on an EKG?

- Multiple foci within the atria are firing at a rate >100
- Basically same thing as wandering atrial pacemaker but fast
- Irregularly irregular
- P waves vary
- P-R interval varies
- R-R interval varies
- P:QRS is 1:1

What’s this rhythm?
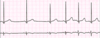
Sinus arrythmia

What is going on with wandering atrial pacemaker and how do you identify it on an EKG?

- Pacemaker changes “spots” within the atria
- Rhythm is irregular
- Shape of P waves vary
- P-R interval varies
- P:QRS is 1:1
- At least 3 different P-waves within 1 lead are needed to make dx
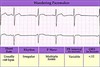
Name that rhythm: Tachycardic, wide QRS complexes of varying amplitudes, “twisted ribbon”
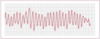
Torsades de pointes
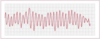
What is this rhythm?

Atrial Flutter
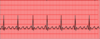
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) will show up on an EKG with regular atrial and ventricular rhythm, narrow QRS, and a HR between _____ and _____ bpm.
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) will show up on an EKG with regular atrial and ventricular rhythm, narrow QRS, and a HR between 160-250 bpm.
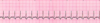
What’s this rhythm?

Sinus arrest

What’s this rhythm?
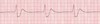
Idioventricular rhythm

What’s this rhythm?

Junctional tachycardia, rate >100

What’s going on with premature atrial contractions (PACs)? How do you identify them on an EKG?

- Irritable site within the atria discharges before SA node
- Identified by:
- Early/premature P wave
- Abnormal P wave differs in shape from a sinus P wave
- QRS complex is nl
- Not an entire rhythm - just a single beat!
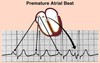
Atrial dysrhythmias are caused by abnormal electrical impulse formation and conduction in the atria secondary to decreased function of the ____________, or an ______________ becomes excited.
Atrial dysrhythmias are caused by abnormal electrical impulse formation and conduction in the atria secondary to decreased function of the SA node, or an ectopic atrial foci becomes excited.
*NOT conducted from the AV node!
What is the normal duration of a PR interval?
0.12-0.20 sec
If every other beat is a PAC, it’s called ___________. If every 3rd beat is a PAC, it’s called _________.

If every other beat is a PAC, it’s called bigeminy. If every 2rd beat is a PAC, it’s called trigeminy (shown).
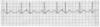
What’s this rhythm?

Wandering atrial pacemaker

What’s this rhythm?

Junctional rhythm, rate ~60

What’s this rhythm?

SVT

Which kind of sinus dysrhythmia is this:
Rhythm: regular
Rate: >100 bpm
P wave: one for every QRS, nl in size/shape/direction
QRS complex: normal (<0.12sec)
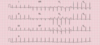
Sinus tachycardia

Describe ventricular tachycardia

- Ventricular rhythm with rate >100 bpm
- Wide QRS and no other discernible waves
- May convert into v-fib or asystole
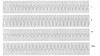
What’s this rhythm?

V-tach

What’s this rhythm?

Atrial bigeminy

What’s this rhythm?

NSR w/ PVC

T/F: atrial dysrhytmias are conducted from the AV node
False!
Abnormal electrical impulse formation and conduction in the atria - ectopic foci
What’s going on here?
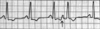
Premature atrial contration (PAC)
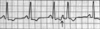
What is the name of this rhythm:
- Single foci in the ventricle acting as pacemaker with a rate of 20-40 bpm
- P waves usually absent (buried)
- QRS wide (>0.12 sec)
- All QRS complexes look the same

Idioventricular rhythm

Atrial flutter is almost always (regular/irregular) rhythm, whereas a-fib is always (regular/irregular)
Atrial flutter is almost always regular rhythm, whereas a-fib is always irregular
What is this rhythm? What’s the rate?

Sinus tachycardia, Rate ~130 bpm

What’s this rhythm?

Multifocal atrial tachycardia

What’s the difference between atrial flutter and a-fib?
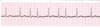
-
Atrial flutter: single irritable atrial foci initiates beat rapidly
- Shows up as saw-tooth p-waves
-
A-fib: 300-600 atrial foci firing at once
- Absence of discernible P waves
- Pictured:

_________ is the most common of all sustained atrial arrhythmias
A-fib! It’s present in 3-4% of the population >70 yrs old
What’s this rhythm?

A-fib

V-fib ain’t so bad, right?
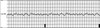
*face palm*
- Chaotic rhythm originating in the ventricles
- Quivering heart = no contraction, no pulse, no cardiac output
- EKG with chaotic deflections, no nl waveform present
- Causes immediate syncope & death within minutes
- Presenting rhythm in 70% of cardiac arrests

An inverted, late, or missing p-wave is indicative of a _______ rhythm.
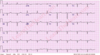
An inverted, late, or missing p-wave is indicative of a junctional rhythm.
- Rate is usually slow: 40-60 bpm
- But can be accelerated: 60-100 bpm
- Can also be tachycardic: >100 bpm
- P-wave sometimes inverted because of the retrograde impulse coming up from the AV node

What’s this rhythm?

V-fib

What is a premature junctional contraction?

- An early beat generated from the AV node.
- Just an event, not a rhythm!
- Shows up as a single inverted P-wave



