CNS infections Flashcards
What is acute encephalitis an infection of?
The brain parenchyma
What cells would you see in the CSF of a patient with acute bacterial meningitis?
Neutrophils
What is the most common cause of viral meningitis?
Enteroviruses such as ECHO
What is the treatment for viral meningitis?
Supportive treatment - generally a self limiting condition
How do you confirm a diagnosis of viral meningitis?
Viral stool culture Throat swab CSF PCR
List some causes of viral encephalitis?
Herpes Simples Varicella zoster CMV HIV Measles West Nile Virus Tick borne encephalitis Rabies
What is the treatment of herpes simplex encephalitis?
High dose IV aciclovir
What is the treatment for varicella zoster viral meningitis?
High dose aciclovir
A 20 year old girl who has just recovered from shingles comes to a & e with her Mum. She is confused and is having trouble sleeping. Her mum says this started last night.
Viral encephalitis due to varicella zoster virus
A 20 year old girl who has just recovered from shingles comes to a & e with her Mum. She is confused and is having trouble sleeping. Her mum says this started last night What investigations would you want?
Lumbar puncture MRI If she has had a seizure then EEG
A 20 year old girl who has just recovered from shingles comes to a & e with her Mum. She is confused and is having trouble sleeping. Her mum says this started last night. There is going to be a four hour wait to get any investigations. What do you do?
Start aciclovir
A 32 year old women presents to a & e with confusion. She also had a widespread blistering rash. This is the MRI of her brain; describe it and give the most likely diagnosis.
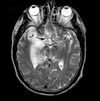
Viral encephalitis due to varicella zoster virus.
MRI shows an inflamed portion of the temporal lobe involving the uncus and parahippocampus (the birght white section)
A patients presents with syptoms suggestive of viral encephalitis. You are concerned that the patient has raised ICP. What investigation is best to perform.
CT scan. In a normal case a lumbar punture should be performed but if there is a concern about raised ICP a CT scan should be given first.
What is the first line investigation for a patient with suspected viral encephalitis (Normal ICP)
LP
What are the three most common causes of bacteria meningitis in neonates?
Listeria
Group B stre
E coli
What is the most common cause of bacterial meningitis in children?
H. Influenzae
What is the most common cause of bacterial meningitis in people aged 10 - 21?
Meningococcoal
What are the two most common causes of bacterial meningitis in people over 21?
Pneumococcal
Meningococcal
What are the two most common causes of meningitis in the elderly?
Pneumococcal
Listeria
What kind of bacterial meningitis is someone who has had a fracture of the cribriform plate at risk of?
Pneumococcal
What kind of bacterial meningitis is someone who has had open head trauma or open neurosurgery at risk of?
Staphylococcus
Gram Negative rods
List 4 things that can be predisposing factors for bacterial meningitis
- Immunocompromised state
- Basilar skull fracture
- Head trauma/Post neurosurgery
- CSF shunt


