Chapter 4: Tissues Flashcards
Define “Tissue”?
A group of similar cells specialized to perform a specific function.
Histology is…
The study of tissues
Four main types of tissues are…
- Epithelial
- Connective
- Muslce
- Neural
Epithelial tissues locations
These tissues…
- cover surface of body (think skin)
- Line various spaces and passageways of the body
- Lining hollow organs
- Body cavities
- Lining of tubes such as blood vessels
- Used to make glands around the body
General Functions of Epithelial Tissues:
- Form Protective barriers
- Control permeability
- Produce specialized secretions
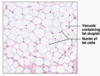
This epithelial tissue type is one layer of flatten cells.

Simple Squamous
This tissue type is ONE layer of cells about as tall as they are wide…

Simple cubodial epithelium
This simple epithelium is one layer of tall, narrow cells…

Simple columnar epithelium
multiple layers of “smaller” cells with upper layers of flattened cells.

Stratified Squamous epithelium
two or more layers of cells about as tall as they are wide.

Stratified cuboidal epithelium
two or more layers of tall, narrow cells…

Stratified Columnar
Function of simple squamous epithelium

allows for rapid diffusion, filtration, and secretions in serous membranes
Where are some of the locations/places simple squamous can be found?

- Air sacs in lungs
- Lining of heart chambers
- lumen of blood vessels
- Serous membranes of body cavities
*these are just some of the examples from the book but it’s beneficial to think about what do all of these mentioned tissues have in common?*
Function of simple cubodial?

Absorption and secretion
Locations of simple cubodial?

- Kidney tubules
- Thyroid glad follicles
- Ducts and secretory regions of most glands
- Surface of ovary
make a note of what these areas have in common. What do these areas of the body do a lot of??
Structure of Nonciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium

Lets brain it down…
No cilia = nonciliated
Columnar = “tall”
Simple = means single layer
*additionally these may contain_goblet cells that secret mucin_*
Function of Nonciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
- Absorption
- Secretion (additionally; secretion of mucin)
Location of Nonciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium

Lining of most of the digestive tract.
*lining of stomach however; does not contain goblet cells*
Structure of Ciliarted Simple Columnar

Single layer of…
- tall
- narrow
- ciliated cells
- Oval-shaped nucleus that runs lengthwise in the basal region of the cell.
- Goblet cells may be present
Function of Ciliated simple columnar epithelium
- Similar to nonciliated, can secrete mucin because they may contain goblet cells
- Movement of mucus along apical surface of epithelium by action of cilia
*
Location of Ciliated Simple Columar Epithelium
Lining of uterine tubes and larger bronchioles of repiratory tract.
Structure of Pseudostratified Columnar Epthelium

- Single layer of cells with varyingheights that APPEARS multilayerd
-
ALL cells connect to the basement membrane. (think bottom surface of cells)
- But not all cells reach the apical surface. (think top surface).
************
Ciliated pseudostratified (contains goblet cells)
Nonciliated pseudostratified (does not have goblet cells of cilia)
don’t confuse pseudostratified with simple. Remember that simple nonciliated can have goblet cells
Location of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?

Ciliated forms lines most of repiratory tract…
- Trachea
- Bonchi
- Larynx
- Pharynx
Locations of nonciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
Lines epididymis and part of male urethra. (not as abundant in the body as ciliated)