Ch 7: Bone Tissue Flashcards
Exam 2 Review
The study of bone is known as
Osteology
Bone is both a _______ and an _______.
tissue, organ
The skeletal system is composed of
- bones
- cartilages
- ligaments
Ligaments connect
bone to bone
Tendons attach
muscle to bone
What are the 6 functions (w/ brief description) of the skeleton?
- Support - hold up body, support muscles
- Protection - brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs
- Movement - limb movements, breathing, action of muscle on bone
- Electrolyte balance - calcium (nerve production, muscle contraction) and phosphate ions (bone modeling and remodeling)
- Acid-base balance - buffers blood against excessive pH changes
- Blood formation - red bone marrow is the chief producer of blood cells
Bone what type of tissue?
osseous
Individual bones consist of…
- bone tissue
- bone marrow
- cartilage
- adipose tissue
- nervous tissue
- fibrous connective tissue
What are the four general types of bones?
- flat
- long
- short
- irregular
Characteristics of flat bones:
- protect soft organs
- curved, but wide and thin
- ex. sternum
Characteristics of long bones
- longer than wide
- rigid lvers acted upon by muscles
- ex. femur or humerus
Characteristics of short bones:
- equal in length and width
- glide across one another in multiple directions
- ex. tarsal bone
Characteristics of irregular bones
- elaborate shapes that do not fit into other categories
- ex. tarsals, carpals, sacrum
Define bone feature:
Compact bone
dense outer shell of long bone
Define bone feature:
diaphysis
shaft cylinder of compact bone
Define bone feature:
medullary cavity
space in the diaphysis of long bone that contains bone marrow
Define bone feature:
epiphyses
enlarged ends of long bone which are strengthened for joint, ligament and tendone attachments
Characteristics of spongy bone:
- spongelike appearance
- spaces are filled with red bone marrow
- few osteons
- provides strength with minimal weight
Define bone feature:
articular cartilage
- layer of hyaline cartilage that covers the joint surface where only bone meets another
- allows joint to move more freely and relatively friction free
Define bone feature:
nutrient foramina
minute holes in the bones surface that allow blood vessels to penetrate
Define bone feature:
periosteum
External sheath that covers bone except where there is articular cartilage
What are the two layers of periosteum and their general function?
- outer fibrous layer - attach to tendons
- innter osteogenic layer - bone forming cells important for growth and healing of fractures (stem cells are in this layer)
Define bone feature and general function:
endosteum
- thin layer of reticular tissue lining marrow cavity
- has cells that dissolve osseous tissue and others that deposit it
Define bone feature and general function:
epiphyseal plate
- Area of hyaline cartilage that separates the marrow spaces of the epiphysis and diaphysis.
- enables growth in length of bone
Define bone feature:
epiphyseal line
A bony scar in adult bone that marks where the growth (epiphyseal) plate used to be
ID: 1

epiphysis
ID: 2

diaphysis
ID: 1

Articular cartilage
ID: 2

red bone marrow
ID: 3

epiphseal plate/line
ID: 4

marrow cavity
ID: 5

yellow bone marrow
ID 6:

periosteum
ID: 7

nutrient foramen
ID 8:

endosteum
ID: 9

compact bone
ID: 10

spongy bone
ID: 11

epiphyseal line/plate
ID: 12
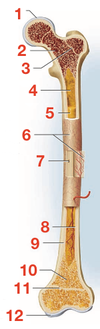
articular cartilage
Define bone feature and general function:
Diploe
- The spongy bone between the inner and outer compact bone of the skull.
- Absorbs shock
- Marrow spaces lined with endosteum
Bone is a _______ _______ that consists of _____, _____, and _______.
- connective tissue
- cells
- fibers
- ground substance
What are the four principal types of bone cells?
(with general function)
- osteogenic cells - create osteoblasts
- osteoblasts - create bone forming cells
- osteocytes - regulate bone remodeling
- osteoclasts - bone desolving
Osteoclasts are responsible for
resporption and reabsorption
In bone remodeling, osteoclasts are responsible for
breaking down bone.
In bone remodeling, osteoblasts are responsible for
bone rebuilding
The matrix of osseous tissue is 1/3 _____ and 2/3 ______.
organic, inorganic
Rickets is
soft bones due to deficiency of calcium salts
Osteogensis imperfecta:
Also known as brittle bone disease. Excessively brittle bones due to the lack of protein & collagen
Red marrow is also known as
myeloid tissue
The hemopoietic tissue of red marrow produces
red blood cells
Red marrow that turns into fatty marrow is called _______ _______.
yellow marrow
True or False
Yellow marrow produces red blood cells
False
Nutrients get into the bone via the _______ _______ and reach the central veritcal canals through transverse perforating canals called _______ ________.
nutrient formina, Volkmann canals.
Where is bone marrow found?
In the central cavities of long bones and in the trabeculae of spongy bone
Ossification (or osteogenesis) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells called ______.
osteoblasts
True or False
Bones only grow in length throughout a person’s life.
FALSE
The grow in width and length
The epiphyseal plate is made of…
hyaline cartilage
The epiphyseal line is made of…
bone
True or False
The epiphyseal line is where bone growth is occuring.
FALSE
The line forms after the growth is complete and the cartliage has turned to bone.
Interstitial growth refers to bone growth in what direction?
length
Appositional growth refers to bone growth in what direction?
Width
Punching wood to build up tissue through stress is an example of…
Wolff’s law of bone
Wolff’s law of bone states that the architecture of bone is determined by _______ stresses placed upon it and the bones adapt to withstand those stresses.
mechanical
Achondroplastic dwarfisim efects the growth of…
long bones
What type of dwarfism is results in a dwarf with normal proportions?
Pituitary dwarfism
Calcium levels are maintained by the hormones ______ and _____ / _____
Calcitonin, Calcitriol / PTH (parathyroid hormone)
Osteoblasts _______ bone.
build
Osteoclasts _______ bone.
dissolve
Osteoblasts takes Ca2+ + PO43- (calcium phosphate) from _______ and puts it _____.
blood stream, bone
Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts work together to maintain _______.
calcium homeostasis
Calcitriol and PTH ________ calcium and phosphate in _______.
increase, blood
Calcitonin ________ calcium and phosphate in _______.
decreases, blood
As calcium increases, phosphate _______.
increases as well.
True or False
If there is an increase of calcium phosphate in blood, it has no effect on bone.
FALSE.
An increase in either calcium phosphate in blood causes a decrease of it in bone and vise verse
Osteoblast activity = a _______ in PTH/Calcitriol activity.
decrease
Osteoblast activity = a _______ in calcitonin activity.
increase
Osteoclast activity = a _______ in calcitonin activity.
decrease
Osteoclast activity = a _______ in PTH/calcitriol activity.
increase
Osteoclast activity takes calcium phosphate from _____ and puts it into _____.
bone, blood
Osteoblast activity takes calcium phosphate from _____ and puts it into _____.
blood, bone
Mineral resorption is the process of dissolving bone and
releasing minerals into the blood
Phosphate is a component of
- DNA
- RNA
- ATP
- Phospholipids
- pH buffers
Calcium is needed in…
- neuron communication
- muscle contraction
- blood clotting
- exocytosis
A break in the bone where the bone hasn’t moved out of place is called a
nondisplaced fracture
A break in a bone that has resulted in in being out of natural alignment is called a
displaced fracture
A break in a bone in multiple places is called a
comminuted fracture
A break in the bone that has penetrated the skin is called a
compound fracture
A partial break in a bone that is not displaced (usually found in children) is called a
greenstick fracture
What are the four steps of a bone healing a fracture?
- Hematoma formation
- Soft callus formation
- Hard callus formation
- Bone remodeling
A procedure in which the bone fragments are manipulated into their normal positions without surgery is called
closed reduction
When fixing a fracture involves surgical exposure of the bone and the use of plates, scres or pins to realign the fragments, it is called
open reduction
What is used to stablize and immobilize a healing bone?
a cast.
What method of treatment is used to treat fractures of the femur or hip in children?
Traction
What treatment accelerates repair of bone healing by suppressing effects of parathyroid hormone?
electrical stimulation
Osteoporosis is a
loss of density due to a loss of organic matrix and minerals
Estrogen _______ osteoclasts
inhibits
Post menapause, osteoclast activity _______.
increases
Hydroxyapatite is also known as…
calcium phosphate
What does Hydroxyapatite do to bone?
makes it hard
Calcium phosphate accounts for ____ of the weight of bone.
2/3


