Cardiology Flashcards
Tx for Brugada Syndrome is:
B blockers
and
ICD
Mitral valve stenosis is most frequently preceded by:
Rheumatic fever which causing thickening of the valve leaflet.
Unstable Tachyarrhythmia should be treated with
Cardioversion
Pt with HTN + CFH should be prescribed what HTN drug(s)
Thiazide + B blockers
Pathophysiology of AO dissection:
Tear in the tunica intima
Blood collection b/w tunica intima and tunica media creating false lumen.
Preffered position in patients with pericarditis is
Sitting up, leaning forward.
Tricuspid valve stenosis is usually seen in conjunction with
Mitral valve stenosis
Presentation of AO dissection is:
Sudden onset of tearing chest pain, between scapulas
AO valve regurgitation murmur best heard in what position?
Right sternal border (2nd interspace)
Pt. leaning forward.
Medications that can be used to treat HTN in pregnancy are:
Labetalol
Methyl Dopa (alph 2 agonist)
any Calcium Channel Blocker
Sx of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy are:
Dyspnea on exertion
Syncope/dizziness
Crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur
S4 gallop
Ventricular stiffness
potassium sparing diuretics and ACE inhibitors used together may produce ________
HyperKalemia
Physical findings associated with Pulmonary valve regurgitation are:
Mild cases are well tolerated and have few or no symptoms Severe cases may have right ventricular hypertrophy Severe cases may have right heart failure Widely split S2 ECG may show right ventricular hypertrophy
Flutter rate is
250-300 bmp
Amyloidosis and Sarcoidosis are known to cause:
Restrictive CM
Treatment for DVT in a pregnant pt is:
Lovenox
Warfarin/coumadin CAN NOT be used at it crosses the placenta!!!
Sick Sinus Syndrome is treated with:
Pacing
Tx of Systolic/Dialated CHF:
ARBs or ACE Inhibitors (vasodilators)
Beta Blockers (lowers mortality)
Digoxin (does not lower mortality)
Which medication is contraidicated in pts with inferior MI:
Nitroglycerin (reduces preload)
inferior MI may be a Rt side MI which are preload dependend
Nitroglycerin may lead to severe drop in blood pressure
Intravenous hydration is indicated in preload depended MI
Normal mean arterial pressure is:
70-100
Valve Locations: Aortic Valve, Pulmonic Valve
Aortic 2nd Rt interspace
Pulmonic 2nd Lt interspace

Waterhammer/ Corrigan’s pulse is associated with
Aortic Valve Regurgitation
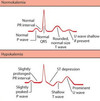
Signs of HyperKalemia seen on ECG are:
peaked T waves
QRS widening
p wave flattening
will eventually transform to V tach or V fib if not corrected.

Tx of acute CHF
ACE-I
Loop diuretics
Nitrate
Oxygen
Morphine