Carbon and Hydrocarbons Flashcards
functional group
atom or group of atoms that is responsible for specific properties of organic compound
hybridization
combination of 2 orbitals at same energy level of same atom
creates new orbital shape
catenation
bonding of atoms of same element into chain or ring
isomers
compounds with same chemical formula but different chemical names and structural formulas
distinguished by different boiling points
structural isomers
compounds wherein position of only 1 atom or bond is moved in structure of compound
stereoisomers
compounds which differ in spatial arrangement of atoms
cis isomers
stereoisomers with matching atoms or groups attached to different carbon atoms on different side of double bond
matching atoms or groups are on same side of carbon chain
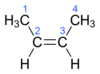
trans isomers
stereoisomers with matching atoms or groups attached to different carbon atoms on different side of double bond
matching atoms or groups are on opposing sides of carbon chain

optical isomers
stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other that are non-superposable
chiral carbon
carbon with all single bonds and 4 different attached atoms
found in optical isomers
aromatic hydrocarbon
compound with only carbon and hydrogen
shaped in benzene ring

alkane
hydrocarbon compound with all single bonds
saturated
alkene
hydrocarbon compound with all single bonds except 1 double bond between carbons
unsaturated
alkyne
hydrocarbon compound with all single bonds except for 1 triple bond between carbons
unsaturated
general formula of alkanes
CnH2n+2
general formula of alkenes
CnH2n
general formula of alkynes
CnH2n-2
allotropes of carbon
diamond
graphite
fullerine
alkyl group
group of atoms formed when 1 hydrogen atom is removed from alkane molecule
saturated hydrocarbon
hydrocarbon in which each carbon atom in molecule forms 4 single covalent bonds with other atoms
unsaturated hydrocarbons
hydrocarbons in which not all carbon atoms have 4 single covalent bonds
aromatic hydrocarbon
hydrocarbon with 6-membered carbon ring and delocalized electrons
benzene
primary aromatic hydrocarbon


