Week 1 Homeostasis Flashcards
(11 cards)
Define homeostasis
Is the maintenance of relatively stable conditions
What are the three basic components of a feed back loop?
- Receptor (sensor) eg skin
- Control centre (integratior) eg brain
- Effector eg shivering
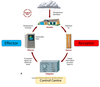
Describe the role of the Receptor in the feed back loop
Detects changes (produced by stimuli) Sends signal to control centre
Describe the role of the Control Centre in the feedback loop
Sets the range of values that the controlled condition should be maintained.
It receives inputs from the receptor and sends signals to the effector if required.

Describe the role of the effector in the feedback loop
This structure receives outputs from the control centre and produces a response that acts to change the controlled condition.

Provide an example of a negative feedback loop and describe it;s role in maintaining homeostasis and normal body function
A stimulus increases body temp (controlled condition) above normal range.
- If body temp decreases (cold), the receptor detects decrease stimuli, sends a messgae to the control centre.
- Reigons of the brain (control centre >)(hypothalamus) recieves signals and evaluates them, then sends impulses to the effector.
- Blood vessels constrict to decrease blood flow to the skin and muscles start to shiver (effectors)

What is the first basic component in the negative feedback loop?
Receptor
Detects changes (produced by stimulus) in the controlled condition and sends a signal to the control centre.

What is the second basic component in the negative feedback loop?
Sets the range of values that the controlled condition should be maintained. It receives inputs from the receptor, evaluates these inputs and send signals to effector.

What is the third basic component in the negative feedback look?
Effector
This structure recieves outputs from the control centre and subsequently produces a response that acts to change the controlled condition.

Describe positive feedback loop
If the response produced by the effector acts to further change the control condition i.e moiving it further away from the normal values, then the whole process is called positive feedback look.
Provide an example of positive feedback and describe it’s role in maintaining homeostasis and normal body function
Blood clotting, say you acquire a cut, the body will release chemicals that begin the process of blood clotting, chain reactions begin to form a clot.
As clotting continues each step releases chemicals that further accelerate the process.
This escalating process is positive feedback loop that ends with the formation of a blood clot.
eg the house is on fire and the fire keeps growing until the problem is solved.



