Muscles Flashcards
(36 cards)
Describe the three basic types of muscle tissue
- Smooth
- Cardiac
- Skeletal

What are the functions of muscle tissue?
Muscles covert chemical energy into mechanical (kinetic energy)
Describe the structure of skeletal muscle
Each of your skeletal muscles is a separate organ composed of muscle fibers.
Tendons are cords of dense irregular CT that attach to the muscle to the periosteum of a bone.
Fascia is a broad band of CT that supports and surrounds muscles - allows free movement, caries nerves and blood and lympatic vessels

Describe how muscle fibres are stimulated to contract
- Motor neuron stimulation of a msucle fibres to produce a muscle action potential. 2. Conversion of the electrical muscle action potential signal to a contraction signal in excitation-contraction coupling. 3. The contraction cycle where myosin pulls on actin and the muscles actually contract
Outline the events that occur at the neuromuscular junction
The nerve signs to the muscle contract at the neuromuscular junction → this then signals a release of acetylcholine) from synaptic end bulb → triggers action potential in the msucle at the motor end plate

Describe the steps involved in muscle contraction
Myofibrils - parallel threads that are contractole elements of the muscle fibre (filaments)
Identify/remember the major muscles of the human body
Agonist muscle: causes desired movement.
Antagonist muscle opposite effect to that of the agonist muscle.

Describe smooth muscle
Found in the walls of hollow internal structures. This tissue is non-striated (smooth) The acts of the smooth muscle are usually involuntary.
Describe the gross structure of a skeletal muscle
Tendon, Fascia.
Beneath the fasicia there are 3 CT that protect and support the muscle:
Epimysium - surrounds the entire muscle
Perimysium - surrounds groups of 10-100+ muscle fibers (fascicles)
Endomysium - surrounds each individual muscle fiber.

How are muscle fibres formed?
During embryonic development muscle fibres are formed by the fusion of 100+ cells called myoblasts, as a result each muscle fibre is a single cell with 100+ nuclei.
→ after fusion muscle fibres loose the ability to divide. Muscle fibres your possess is more or less set before you are born.

How do muscles grow?
Not a result of division. Process called hypertrophy:
The sacrolemma - is the plasma membrane of muscle fibres.
Sacroplasm - the cytoplasm of muscle fibre Transverse (T) tubules: finger like projections of the sacrolemma that extend towards the centre of each muscle
Sacroplasmic reticulum - acts as an internal store for calcium = action potential
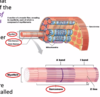
What is the structure of a thick and thin filament?
Thin filaments - 8nm diameter
Thick 16nm they are both arranged in a repeating sequence, they are then arranged into sacromeres (these are the basical functional unit of a muscle)

What supplies the skeletal muscle structure?
Supplied by nerves and blood vessels.
Nerves carry motor neuron axons that control muscle fibre contraction.
Blood vessels bring nutrients and remove wastes
Define myoglobin
The protein that is found only in muscle fibres. It binds and stores oxygen molecules that make their way into the muscle fibre
Define a sacromere
Contractile unit of muscle cell.
Z discs - zigzagging proteins that sperate each sacromere.
The A- band extends the entire length of the thick filaments
The H zone - contains only thick filaments
The zone of overlap - Thick and thin filaments over lapping eachother
The I-band: contains only thin filaments, the Z discs divide this band in the middle
The M-line - a collection of proteins that cold the thick filaments together in the centre of the sacromere

Define the chemistry of thin filaments
Action: is a contractile protein that helps to form the thin filaments, twists into a helix with two regulatory proteins - tropomyosin and troponin.
Actin molecules contain myosin-binding site that allows the interface for myosin (found in thick filaments)
Troppmyosin and troponin: help turn contracts on and off
Describe the chemistry of thick filaments
Contractile protein is myosin, which functions as the motor protein. Myosin is responsible for the movement that will result in muscle fibre contration. Myosin tail, myosin hrad - the heads project towards the thin filaments that surround each thick filament.
What happens during contraction?
Myosin heads of thick filaments pull on actin molecules that forms the thin filaments and this shortens the sacromere producing a contraction. Molecules dont shorten in contraction, they slide across eachother
What happens when an action potential occurs in a motor neuron?
Signals coming from motor neurons, the axons of the motor neurons make contact with muscle fibres at specialised synapses called neuromuscular junction
What is a motor unit?
A motor unit consists of a single motor neuron and all the muscle fibres that it makes synaptic connections with. Muscles that control small, precise movements consist of small motor units. Muscles that are involved in large powerful movements contain larger motor units
What happens when an action potential occurs in a motor neuron?
Depolarisation triggers ana ction potential in the muscle fibres, then action potential propagates across the muscle fibre membrane surface. → The muscle action potential then propogates along the sacrolemma and in the T tubules
What are the 2 steps involved in excitation-contraction coupling?
Excitation-contraction cooupling refers to the steps that link muscle fibre action potentioals (excitation) to muscle fibre contractions. 1. Calcium release 2. Thick-thin filament
What two change occur that allow muscle fibre relaxation?
1.Motor neuron stops firing action potentials. ↓ ACh, ceasing to release Ca2+ ions. 2. Protein pumps on the sacroplasmic reticulum pump Ca2+ ions back into the sacroplasmic reticulum. - Ca2+ from sacroplasm reducing binding to troponin, tropomyosin covers up the myosin binding site on the actin molecule, without myosin binding to actin contraction cannot occur
What are the 2 steps involved in excitation-contraction coupling?
Excitation-contraction cooupling refers to the steps that link muscle fibre action potentioals (excitation) to muscle fibre contractions. 1. Calcium release 2. Thick-thin filament


