SM_27b: Overview of the Cranial Nerves: VII and VIII Flashcards
(16 cards)
Facial nerve enters the ____ of the ____ of the temporal bone
Facial nerve enters the internal acoustic meatus of the petrous part of the temporal bone

Facial nerve (VII) divides into three branches within the temporal bone: ____, ____, and ____
Facial nerve (VII) divides into three branches within the temporal bone
- Greater petrosal: parasympathetics to V2
- Chorda tympani (out of petrotympanic fissue) with taste and parasympathetics to V3
- Facial nerve proper out stylomastoid foramen to muscles (branchiomotor)

Greater petrosal division of facial nerve provides ____
Greater petrosal division of facial nerve provides parasympathetics to V2

Chorda tympani division of facial nerve provides ____ and ____ for V3
Chorda tympani division of facial nerve provides taste and parasympathetics to V3
(anterior 2/3 of tongue)

Facial nerve proper is ____ to the face muscles
Facial nerve proper is branchiomotor to the face muscles

Nevus intermedius is ____
Nevus intermedius is smaller root of VII for taste and parasympathetic fibers in between the larger branchiomotor root and the vestibulocochlear nerve

Describe facial nerve distribution
Facial nerve distribution
- Temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, and cervical nerves are more geographic territories than specific facial nerve branches
- All within substance of parotid gland

Depressor anguli oris goes to ____, while depressor labii inferioris goes to ____
Depressor anguli oris goes to angle, while depressor labii inferioris goes to lower lip

Bell’s Palsy affects the ___ nerve and often results from ___
Bell’s Palsy affects the facial nerve and often results from Herpes infection
- Have patient make a face to contract muscles -> expressionless on affected side
- Cannot close eye, hard to keep food / liquid in mouth (orbicularis oris / buccinator lost on affected side)
- Taste and lacrimal gland may also be affected

____ is pretrematic branch for facial nerve
Chorda tympani is pretrematic branch for facial nerve

Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) exits through ____ of ____ part of temporal bone
Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) exits through internal acoustic meatus of petrous part of temporal bone
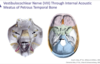
Auditory / Eustachian tube leads from the ____ to ____
Auditory / Eustachian tube leads from the pharynx to middle ear

Cochlear nerve division of CN VIII goes to ____ for ____
Cochlear nerve division of CN VIII goes to cochlea for hearing

Vestibular nerve division of CN VIII goes to ____ for ____
Vestibular nerve division of CN VIII goes to vestibular apparatus (semicircular canals) for sense of balance and motion

Primordium of vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) is ____
Primordium of vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) is otic placode (ectoderm)
- Otic placode sinks under the surface to form the otocyst, which is the primordium for the inner ear

Otocyst forms the ____ and shapes into the ____ and ____
Otocyst forms the inner ear and shapes into the cochlea and semicircular canals



