Rheumatology/Orthopedics & Sports Flashcards
(94 cards)
Ecthyma gangrenosum
Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Rapidly progressive skin lesions that develop into nontender nodules with central necrosis
Seen in immunocompromised patients
Neurogenic claudication
Symptom of spinal stenosis
Characterized by pain with extension of the spine (walking, prolonged standing)

Dermatomyositis
Distinguishing features of fibromyalgia, polymyositis, and polymyalgia rheumatica
- Clinical features
- Diagnosis

Manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus
- Clinical symptoms
- Laboratory findings

Meniscal tear
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Exam
1. Causes
Results from twisting injuries
2. Symptoms
Impaired extension of the Knee
Instability
Exacerbation of pain with squatting
3. Examination
Joint line tenderness
Effusion
Locking or catching when joint is extended under load
Provocative maneuvers for meniscal tear

What structure is at risk?

Midshaft fracture of the humerus
Risk of damage to radial nerve (runs in groove on dorsal aspect of humerus)
- Wrist and finger extensors
- Sensation in dorsum of hand
Differential diagnosis of septic arthritis
Gram positive organisms: Younger age, no IV drug use
-staph aureus
Gram negative organisms: Older age, IV drug use
- E. coli
- Pseudomonas
Septic arthritis
- Risk factors
- Clinical features
- Diagnosis
- Initial treatment
Granulomatosis with polyangitis
- Clinical manifestations
- Diagnosis
- Management
White individuals 30-50


Pyoderma gangrenosum
Cutaneous manifestation of granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura (HSP)
Half of cases are preceded by an upper respiratory infection
Ileo-ilial intussusception

Granulomatous vasculitities in children
Takayasu arteritis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener)
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss)

Strawberry tongue, feature of Kawasaki disease
Diagnostic criteria (fever for >=5 days with >=4 of the following findings)
Oral mucous membane changes (e.g., strawberry tongue, cracked lips)
Bilateral nonexudative conjunctivities with limbal sparing
Cervical lymphadenopathy (>1.5 cm node)
Polymorphous rash
Erythema or edema of the hands and feet
Treat with IVIG + aspirin
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
- Symptoms
- Treatment
Symptoms
Headaches
GI symptoms
Non-pruritic petechial rash that begins on extremitis (including palms/soles) and spreads centripetally
Fever
Conjunctival injection
Treatment
Doxycycline
Koplik spots (small white spots on bucal mucosa)
Classic in measles
Forscheimer spots (petechiae on soft palate)
Rubella
Tinel sign
Phalen test
Provocative tests for carpel tunnel syndrome (compression of median nerve)
Tinel sign: Precussion over the median nerve at the risk
Phalen test: Holding hands in extreme flexion
Risk factors for carpel tunnel syndrome
Obesity
Diabetes
Hypothyroidism
3rd trimester of pregnancy
De Quervain tenosynovitis
Overuse of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor poolicis longus
Causes pain at the base of the thumb
Common after pregnancy due to lifting the newborn
Provocative maneuver: Finkelstein test

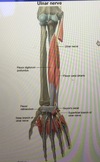
Ulnar nerve compression at the elbow
Compression occurs in the epicondylar groove (due to direct pressure) or the cubital tunnel (due to repetitive or prolonged flexion of the elbow).
Symptoms: Paresthesias in the 4th and 5th fingers and the medial forearm, and weakness of intrinsic hand muscles.

Roseola infantum
- Microbiology
- Epidemiology
- Clinical features
- Treatment


Kocksackie virus