Radiology Flashcards
5yo with ataxia, vomiting, and headache
Differential diagnoses and most likely diagnosis?

Differential:
Ependymoma
Juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma
Medulloblastoma.
Most likely:
Ependymoma - 4th ventricle mass, expanding through Magendie and Luschka foramina. Can calcify and have cystic components. Nonhomogeneous contrast enhancement.
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
Child with complex partial seizures
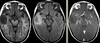
Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor (DNET)
Non-enhancing T2 bright, T1 hypodense temporal lobe mass
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
25 yo with neck stiffness and headache

Ruptured dermoid cyst
Fat in the ventricles is pathognomic
Chemical meningitis
20-30yo dermoid; 40-50yo epidermoid
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
CPA mass
Diagnosis?
Hint: Pay careful attention to the density/intensity pattern

CPA Lipoma
Hypodense on CT (fat attenuation)
Hyperintense on T1
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
17 yo with new partial seizures
Diagnosis?
Other differential diagnoses?

Ganglioglioma
Faint hypointense T2 FLAIR signal without significant mass effect or edema
Bright gyriform enhancement on T1
Can also be cystic or calcified
When these occur in the cerebellum=Lhermitte-Duclos Disease
Differential: DNET, gangliocytoma, oligodendroglioma, focal encephalitis
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
Man with sleep apnea

Clival chordoma
Abnormal isointense T1 signal mass involving the entire clivus
Contains physaliphorus cells
Other Differential: Metastasis, lymphoma, multiple myeloma
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
48 yo with subacute myelopathic symptoms (heavy feeling in legs that improves with rest, difficulty standing, paresthesias, urinary symptoms, back pain)
Diagnosis and eponym?

Spinal cord dural AVM
Foix-Alajouanine syndrome
Intradural Serpentine flow voids along surface of spinal cord
Angiogram: Enlarged draining vein
Spinal cord: Diffuse hyperintense T2 intramedullary signal
Symptoms due to venous hypertension
(Note: If blood vessel flow voids appear to be in subarachnoid space and angiogram shows a fistula, then consider spinal dural AV fisula)
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
72yo with severe neck pain.
Diagnosis?
(Neoplastic, infectious, traumatic, or degenerative?)

Ossified Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
Calcified, vertically oriented structure in the anterior aspect of the spinal canal
Degenerative
Can cause severe spinal stenosis and cord/nerve root compression
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
8yo with first time seizure
Diagnosis?
Other associated findings?

Sturge-Weber Syndrome
Congenital phakomatosis with hemangiomatosis of face (CN V distribution), choroid of the eye, and leptomeninges
“Tram-track” Cortical calficifications, often with parenchymal volume loss due to vascular steal
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
Diagnosis?
Genetics?

Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (aka
Optic nerve enlargement = glioma
T2 hyperintese spots in cerebellum = NF spots
Chromosome 17, Autosomal dominant
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
Otherwise well baby with macrocephaly
Imaging abnormality and likely etiology?

Hydrocephalus and congenital aqueductal stenosis
Large lateral ventricles with “dangling choriod plexus sign”
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
Dysmorphic baby
Diagnosis?

Holoprosencephaly
(often associated with missing nose, single eye, and other midface abnormalities)
Large monoventricle, fused thalami, absence of falx
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
Baby born to mother with hypercoagulable disorder
Diagnosis?
Etiology?

Hydranencephaly
No cerebral hemispheres visualized
but Falx, thalami, and midbrain are intact
In-utero ACA and MCA strokes
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
15 month old boy with progressive loss of milestones
Diagnosis, Genetics, Clinical features, and Treatment?
Other differential diagnoses?

Leigh disease (subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy)
Mitochondrial disorder, due to nuclear (autosomal or X-linked) or mito DNA mutations affecting oxidative phosphorylation (ex. pyruvate dehydrogenase, pyruvate decarboxylase, or cytochrome C oxidase)
Clinical features: Lactic acidosis, hypotonia, ophthalmoparesis, cardiomyopathy
Treatment: Bicarb/citrate, thiamine, ketogenic diet
CT: Hypodense basal ganglia
MRI: T2 hyperintense basal ganglia (GP/putamen/caudate)
MRS: reduced NAA, elevated lactate
Can look similar to Wernicke’s but spares mammillary bodies and red nuclei
Other differential diagnoses:
methanol and Wilson’s: T2 hyperintensities in putamen
carbon monoxide and cyanide poisoning: T2 hyperintensities in globus pallidus
Kearn-Sayne syndrome
(thanks fo Raf Llinas)
65yo man found dead in bed, wife attempts to cash in new $1 million life insurance policy hours later
Likely diagnosis?
Other considerations?

Carbon monoxide poisoning
CT: hypodense basal gangila (especially globus pallidus)
MRI: T2 bright basal ganglia, especially globus pallidus, can restrict diffusion acutely
(note also diffusely T2 dark white matter, another CO feature)
Other differential diagnoses: Cyanide poisoning (globus pallidus)
methanol toxicity or Wilson’s disease (but generally involve putamen)
(thanks to Raf Llinas)
Elderly woman develops chorea during a prolonged hospitalization for bowel resection
Diagnosis?
Why does this condition result in this MRI signal pattern?
Other conditions that can have this?
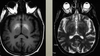
TPN-related manganese toxicity
Manganese is bright on T1, normal to dark on T2
Wilson’s disease (copper) can sometimes have T1 bright putamen (sometimes globus pallidus), too, but will be definitely be T2 bright. “Face of giant panda” in midbrain
PKAN/NBIA (iron): T1 slightly bright, T2 dark globus pallidi; can see iron on SWI imaging; “Eye of the tiger”
Basal ganglia calcifications are also T1 bright (TORCH infections, Toxo, Fahr disease, etc)
Hemorrhage can be T1 bright (for example, CO poisoning could cause hemorrhage)
(thanks to Raf Llinas)


