nutritional and toxic disorders Flashcards
reward center involved in addiction
ventral tegmental area dn nucleus accumbens.
Opioid receptors involved in spinal anasthesia
kappa
opioid receptor involved in supraspinal analgesia
mu1
opioid receptor involved in euphoria and respiratory depression
mu2
mechanism of action of amphetamines
induces direct release of dopamine and norepi, and inhibits their reuptake.
mechanism of action of cocaine
inhibits presynaptic reuptake of dopamine, seratonin and norepinephrine .
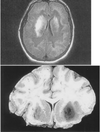
pathologic findings in Wernike’s encephalopathy
patechial hemorrhage in mammillary bodies, hypothalamus, medial thalami, and periaqueductal grey matter
mechanism of action of EtOH
stimulates GABAa receptor
time frame of minor withdrawal symptoms after last drink
6-36 hours
time frame of seizures after last drink
6-48 hours
time frame of delirium tremens after last drink
48-96 hours
mechanism of action of caffeine
competitively antagonises Adenosine A1 and A2A receptors, increases excitatory neurotransmitter release.
hypertension, tachycardia, nystagmus, decreased pain sensation, bizarre behavior.
Phencyclidine (PCP) intoxication
mechanism of action of Phencyclidine (PCP)
non-competitive antagonism at NMDA receptors
mechanism of action of most halluncinogens
work at seritonin receptors
pupillary findings in hallucinogen use
midriasis
prolonged use destroys seritonergic neurons
Ecstasy
genetic disease associated with low Vit E levels
abetaliporoteinemia
biochemical reaction that vit B12 is important for
conversion of homocysteine to methionine
distal sensorimotor axonopathy, scaly rash, garlicky breath
arsenic poisening
GI symptoms, neuropathy with autonomic features, alopecia
Thallium poisoning
headache, anxiety, encephalopathy, almond taste
cyanide poisoning
behavior change, tremor ataxia, inflamed gums, excessive salivation
mercury poisoning
what type of poisoning?

carbon monoxide poisoning- necrosis of globus pallidus and subcortical white matter