Proteins Flashcards
What are the 2 stages of protein synthesis?
Transcription and Translation
What is transcription in protein synthesis?
The transfer of genetic instructions in DNA to mRNA in the nucleus
What is translation in protein synthesis?
The process in which the genetic code in mRNA is read to make a protein at the ribosome.
What are codons?
The 3 letter sections of mRNA which code for blocks of proteins called AMINO ACIDS
How many amino acids are there?
20
Amino acids have a central carbon atom surrounded by which 3 things?
An amino group
A carboxyl group
A variable group (the R group)

What are the monomers of proteins?
the Amino Acids
Amino acids join together to form a polymer called a ____________
polypeptide (or a protein)
A condensation reaction is also called a _________
Dehydration reaction
two amino acids join together by forming a __________ bond
peptide
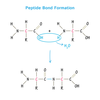
What is a polypeptide?
It can be a few amino acids bonded together or it can be thousands.
What are complex proteins?
Multiple polypeptide chains that are twisted and tangled together.
What is the primary structure of a protein?
It is the basic amino acid sequence

What are the secondary structures of proteins?
The secondary structure occurs when hydrogen bonds between nearby amino acids form creating structures called beta-pleated sheets and alpha helixes.

Beta pleated sheets are found in the protein (silk) that spiders use to make their webs

Alpha helix shape can be found in keratin (the protein found in our hair and finger nails)

What are the tertiary structures of proteins?
The further folding together of polypeptide. It’s held together by interactions between the R-Groups of the amino acids.
It is still one single consistent strand of amino acids.

What are quarternary structures of proteins?
This is when more than 1 polypeptide strand with tertiary structure is folded and tangled together.

What types of bonds hold protein structures together?
Hydrogen Bonds
Ionic Bonds
Covalent Bonds
Disulphide Bridges
(only if the R-groups contain sulphur)
What are the proteins with almost exclusively primary and secondary structures only?
Keratin and Silk (spider web)
What are globular proteins?
The proteins of tertiary and quarternary structures that have folded into round/globe shapes
What type of protein is hemoglobin?
a protein made of 4 separate peptide units in a quaternary structure

What is denaturation?
When a protein loses its normal shape or configuration.
What conditions cause denaturation?
Excessive Heat
Extremes of pH
Heavy Metal Exposure


