Cell Structure II Textbook Flashcards
(48 cards)
What does protoplasm refer to?
It is a collective term that references the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
It refers to all the substances within the cell.
What is the cytoplasm?
the region of the protoplasm outside of the nucleus and the location where nutrients are absorbed, transported and processed
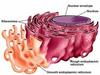
What is the cell membrane?
the edge of the living cell.
composed of a double layer of lipid or fat molecules and embedded proteins.
It provides the cell with a connection to the external environment.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
It holds the contents of the cell in place and regulates the movement of molecules into and out of the cell.
It also contains receptor sites, which serve as docks for the entry of molecules that affect cell activity.
Why is the cell membrane selectively permeable?
Because it only lets certain things pass through.
Ex. Water & Small non-polar molecules (O2, CO2)
Prevents charged particles (H+, Na+, Cl-, amino acids, glucose) from diffusing through
What are embedded proteins in a cell membrane?
Wholly or partially embedded proteins within the phospholipid bilayer.
Form protein pores to allow small charged ions and large polar molecules to diffuse in/out of the cell
Act as pumps - actively transporting molecules (requires energy - ATP)
What are glycolipids?
Carbohydrates attached to a phospholipid
Serve in cell recognition (antigens) and receptor (docking) sites on the cell membrane
Only found on the cell membrane
What are glycoproteins?
Carbohydrates attached to an embedded protein
Serve in cell recognition (antigens) and receptor (docking) sites on the cell membrane
Only found on the cell membrane
How is cholesterol used in the cell membrane?
it helps maintain the structure and fluidity of the membrane
The cholesterol molecules disturb the close packing of the phospholipids
Reduces permeability to some solutes
What is the nucleus?
It is the control center of the cell.
Controls metabolic functioning of the cell & determines the cell’s characteristics.
It contains chromatin – DNA & proteins – of the cell
What is the nuclear envelope?
it is the membrane that encloses the nucleus
What is a nuclear pore?
An opening in the nuclear envelope to allow large molecules to pass from the nucleoplasm to the cytoplasm.
What are eukaryotic cells?
Cells that have a true nuclear membrane are referred to as eukaryotic cells.
- Plant and animal cells are eukaryotic
What are prokaryotic cells?
Cells that lack a nuclear envelope.
Bacteria and blue-green algae are prokaryotic cells They are the oldest known forms of life.
The hereditary material in prokaryotic cells is spread throughout the nucleus.
What are Chromosomes?
Threadlike structures of DNA that contain genes.
What is Chromatin?
The genetic material of a cell
Made of DNA and Proteins
During cell division, chromatin condenses to form the chromosomes.
What are genes?
units of instruction that determine the specific traits of an individual.
What is the nucleolus?
A small spherical structure located inside the nucleus.
The entire function of the nucleolus is not known but scientists believe that it is involved with the synthesis of proteins in the cytoplasm.
Specialized area of chromatin that produces rRNA which is a component of ribosomes
What are organelles?
Tiny structures within the cytoplasm of cells that carry out various functions to maintain the life process of a cell.
What are mitochondria?
One of the largest organelles within the cytoplasm.
They provide the cells with energy
Often referred to as the “power plant” of the cell.
They are the centers of cell respiration.

What are ribosomes?
One of the smallest of a cell’s organelles
They are the most numerous organelles within the cell.
Site of protein synthesis
Found attached to rough ER or free-floating in the cytoplasm.
What do attached ribosomes do?
Produce proteins for export (exocytosis) out of the cell
What do free ribosomes do?
produce proteins to be used inside the cell
What is the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
A series of canals that carry materials throughout the cytoplasm.
Composed of parallel membranes.
Rough ER - has ribosomes attached to the surface, acts as transport of polypeptides through the cell
Rough ER - Where protein folding occurs
Smooth ER - Does not have ribosomes attached - acts as a transport (like rough ER)
Smooth ER - Contains enzymes to detoxify drugs and alcohol and to synthesize lipids.