Pharynx and Larynx Flashcards
1
Q
Pharynx Function
A
- Directs food into esophagus
- conducts air into Larynx and Trachea

2
Q
Three partsof Pharynx
A
- Nasopharynx
- Respiratory part of pharynx
- Oropharynx
- Laryngopharyx

3
Q
Ostium of the Auditory Tube (Pharyngotympanic/Eustacian Tube)
A
- connects middle ear to nasopharynx
- Torus Tubarius - carilagenous portion Pharyngotympanic tube that extends into nasopharynx

4
Q
Torus Tubarius
A
- Carilagenous portion of Pharyngotympanic Tube that extends into Nasopharynx

5
Q
Characteristics and Components of Oropharynx
A
- Palatoglossal arch seperates oropharynx from oral cavity
- Lingual Tonsil
- Palatine Tonsil
- Valleculae

6
Q
Origin of superior constrictor
A
- Pterygomandibular raphe
- common origin with buccinator muscle

7
Q
Piriform Recess (location)
A
- outpouching lateral to opening of larynx
- Foreign objects can get lodged here

8
Q
Tonsils are collections of what type of tissue?
A
- Lymphoid
9
Q
Types of Tonsils
A
-
Pharyngeal tonsils
- at roof of nasopharynx
-
Tubal tonsils
- ostium of auditory tube
-
Lingual tonsils
- Posterior 1/3 of tongue
- **Palatine tonsils **
- Between pillars of Glossopharyngeal Arches
- tonsillar fossa
10
Q
Tonsillectomies (removing which tonsil and risks)
A
- removing palatine tonsils
-
Risks
- highly vascularized –> excessive bleeding
- can damage glossopharyngeal nerve (lingual branch)
- would lead to altered sensation from posterior 1/3 tongue
11
Q
Tonsil Stones
A
- Calcified collections of cellular debris, bacteria, etc
- Can be cause of bad breath
- ***Only in people with intact palatine tonsils
12
Q
Adenoiditis
A
- enlarged/inflamed palatine tonsils
- breathing difficulty from blocked Chonae
- chronic blockage of auditory tube –> middle ear infections–> hearing loss
13
Q
Pharyngeal constrictors
A
- Superior
- Middle
- Inferior

14
Q
Pharyngeal Raphe
A
- Midline meeting of pharyngeal constrictors
- origin of pharyngeal constrictors

15
Q
A

16
Q
Longitudinal Muscles of Pharynx
A
- Stylopharyngeus
-
Palatopharyngeus
- depresses soft palate and narrows pharyngeal inlet
-
Salpingopharyngeus
- Salpinx = tube (from auditory tube)

17
Q
Innervation of Pharynx
A
-
Motor
- Vagus Nerve
- EXCEPT stylopharyngeus…CN IX (3rd arch muscle)
-
Sensory
- Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX)
- both types of nerves come from pharyngeal plexus

18
Q
Tensor Veli Palatini (Function, Innervation, muscle arch origin)
A
- Closes off oral cavity from nasopharynx when swallowing
- opens auditory tube when yawn/swallow
- Innervation: V3
- 1st arch muscle

19
Q
Levator Veli Palatini
A
- Elevates soft palate
- closes off nasopharynx from oral cavity
- opens auditory tube
- Innervation: Vagus

20
Q
Palatoglossus Muscle
A
- Makes palatoglossal arch when covered with mucosa
- Function: depresses soft palate and narrows pharyngeal inelt

21
Q
Laryngeal Folds
A
- Vestibular Fold - false vocal cord
-
Vocal fold - true vocal fold
- contains vocal ligament

22
Q
Spaces of Interior of Larynx
A
-
Vestibule
- entrance to larynx
- superior to vestibular folds
-
Ventricle
- space between vestibular and vocal folds
-
Glottis
- vocal cords and space between true vocal cods

23
Q
Laryngeal Cartilages
A
-
Thyroid Cartilage
- Laryngeal prominence
- Thyroid notch
- connected to hyoid by thyrohyoid membrane
-
Cricoid Cartilage
- connected to thyroid by cricothyroid membrane
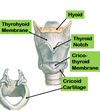
24
Q
Cricothyrotomy
A
- establish emergency airway if other methods dont work
- cut made through skin and cricothyroid membrane
25
Arytenoid cartilages
* 2 of them
* have **anterior muscular process** and **anterior vocal process**
* **Vocal cords** run from **vocal process** to **inner surface** **of thyroid cartilage**

26
Epiglottis
* Seperated from tongue via **valleculae**
* connects to **arytenoid cartilage** via **aryepiglottic folds**

27
Larynx structures Picture

28
Laryngeal Membranes Picture

29
Functions of Larynx
1. Close laryngeal Inlet to keep food out of airway
2. Move vocal cords
30
Laryngeal Muscles
* **Posterior Cricoarytenoid Muscles**
* open airway
* **abduct vocal cords\*\*\*\*\***
* **Oblique and transverse arytenoid muscles**
* close airway, move vocal cords together
* **Cricothyroid -** stretch vocal cords
* **Lateral cricoarytenoid -** adduct cords
* **Vocalis -** fine adjustments of vocal cords

31
CN IX Glossopharyngeal

32
Innervation of Larynx
* **Sensory:** Vagus
* **Internal laryngeal ** - above vocal cords
* **Recurrent laryngeal -** below vocal cords
* **Motor:** Vagus
* EXCEPT **cricothyroid** which gets from **recrurrent laryngeal**
* **Visceral Sensory -** CN IX
*
33
Vagus Nerve Damage
* **Recurrent Laryngeal Damage** - hoarseness, lose of voice
* **Internal laryngeal Damage** - loss of cough reflex


