Neuroanatomy Flashcards
What is the correct term/name for nerve cell bodies in the CNS?
Nucleus
What is the correct term for a bundle of axons in the CNS?
Tract
What is the correct term/name for nerve cell bodies in the PNS?
Ganglion
What is the correct term for a bundle of axons in the PNS?
Nerve
What do spinal nerves supply?
Soma/body wall
Where is the only place spinal nerves are located?
Intervertebral foramina

What is the name given to spinal nerves once they have exited the intervertebral foramina to connect with the body wall?
Rami

What is the name given to the connecting structures attaching the spinal cord and spinal nerves of the same level?
Roots and rootlets

Label these structures


What are nerve plexuses?
Networks of intertwined anterior rami
Which axons are transported in the anterior horn of the spinal cord?
Motor axons
Which axons are transported in the posterior horn of the spinal cord?
Sensory axons
Which segment of the spinal cord has lateral horns and why?
T1 to L2 - transports sympathetic axons
Which nerve is the only sensory nerve not to synapse in the thalamus prior to entering the cortex?
Olfactory
How many layers of scalp are there?
5
What are the layers of the scalp?
S = Skin
C = Connective tissue
A = Aponeurosis
L = Loose connective tissue
P= Pericranium
What is the arterial supply of the scalp?
Scalp branches from the external carotid artery
What is the thinnest part of the skull?
Pterion
Which artery courses over the deep aspect of the pterion?
The middle meningeal artery
What are the three layers of meninges superficial to deep?
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
What is the function of the dura mater?
Protection - this is the toughest meningeal layer
What is the function of the granulations on the arachnoid mater?
Reabsorbing CSF
What is the function of the pia mater?
Adherence to the brain and all nerves & vessels entering or leaving the brain
What is the dura mater adherent to?
The internal aspect of all bones of the skull
What is the tentorium cerebelli?
A tough layer of dura mater ‘tenting’ over the cerebellum
What is the falx cerebri?
A midline structure of dura mater separating the two cerebral hemispheres
Which ventricle is the central canal of the spinal cord continuous with?
4th ventricle
Which ventricle is in the midline?
3rd
Where is the 3rd ventricle located?
It is a midline structure within the diencephalon
What is the cerebral aqueduct?
It connects the 3rd and 4th ventricles in the midline
What two structures does the 4th ventricle lie between?
The cerebellum and pons
Which kind of haemorrhage would rupture of the middle meningeal artery be?
Extradural
Label these structures.


How is the cerebellum attached to the brainstem?
3 peduncles - superior, middle and inferior

What are the three layers of the cerebellum?
Molecular layer (outer)
Purkinje cell layer (middle)
Granular layer (inner)

Which cerebellar layer do afferent projections mainly reach?
Granular layer
What is the only cerebellar layer that efferent signals can travel from?
Perkinje layer
What clinical signs would a patient show if affected by a midline cerebellar lesion?
Disturbance of postural control: will fall over when standing or sitting despite limbs being in correct position
What clinical signs would a patient show if affected by a unilateral hemispheric lesion of the cerebellum?
Loss of limb coordination on the ipsilateral side
May have intention tremour
What clinical signs would a patient show if they suffered bilateral cerebellar dysfunction and what can commonly cause this?
Slowed, slurred speech (dysarthria), bilateral incoordination of the arms and a staggering, wide based gait (cerebellar ataxia)
Alcohol intake
What are the 5 main basal ganglia?
Caudate nucleus
Putamen
Globus pallidus
Subthalamic nucleus
Substantia nigra
What does the lenticular nucleus consist of?
The globus pallidus and putamen
What does the striatum consist of?
Caudate nucleus and putamen
What does the corpus striatum consist of?
Striatum (caudus nucleus and putamen) and globus pallidus
Label these structures.


Label these structures.

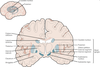
Where is the substantia nigra located?
Midbrain

What are the functions of the basal ganglia?
To allow purposeful movement
To inhibit unwanted movement
Assist in posture and muscle tone
What is the clinical significance of the substantia nigra?
Degeneration of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra is the pathology of Parkinson’s disease
Which side of the body do unilateral basal ganglia lesions affect?
Contralateral side
What clinical signs do basal ganglia lesions show?
Changes in muscle tone
Dyskinesias (abnormal, involuntary movements) including:
- tremor (sinusoidal movements),
- chorea (rapid, asymmetrical movements usually affecting distal limb musculature)
- myoclonus (muscle jerks).
Which white matter tracts in the brain connects cortical sites in the same hemisphere?
Association fibres
The Lumbar Enlargement of the Spinal Cord consists of which spinal nerves?
L1 - S4
Which spinal cord tract governs fine, precise movements?
Corticospinal tract
Which artery do the vertebral arteries arise from?
First part of the subclavian artery
What is this structure?

The circle of Willis
Label these arteries.


What arteries are branches of the internal carotid at the circle of Willis?
Anterior cerebral artery
Middle cerebral artery
What fissure does the middle cerebral artery travel in?
Lateral sulcus
Which artery supplies the basal ganglia?
Striate branches from the middle cerebral artery
What fissure does the anterior cerebral artery travel in?
Medial longitudinal fissure
Which artery connects the anterior circulation in the brain to the posterior?
Posterior communicating arteries
What areas of the brain does the anterior cerebral artery supply?
Medial and superior cerebral hemisphere
All areas shaded in blue

What areas of the brain does the middle cerebral artery supply?
Lateral aspect of the brain
All areas in pink

What areas of the brain does the posterior cerebral artery supply?
Inferior and posterior aspect of the cerebral hemispheres
Cerebellum
Brainstem
All areas in yellow

At what level do the two vertebral arteries join to form the basilar artery?
Inferior aspect of the pons
At what level does the basilar artery split to form the posterior cerebral arteries?
Midbrain
What three artery groups supply the cerebellum?
Superior cerebellar
Anterior inferior cerebellar arteries
Posterior inferior cerebellar arteries
Where do the dural venous sinuses ultimately drain into?
Internal jugular vein
What structures pass through the cavernous sinus?
Internal carotid artery
Cranial nerves III, IV, V (branches V1 and V2) and VI
Where is the superior sagittal sinus located?
Along the margin of the falx cerebri
Which sinus is indicated in red?

Cavernous sinus


