Muma Quiz 1 GI Flashcards
(66 cards)
Antacids Neutralize? Taken when and lasts for? Can affect the absorption of?
Neutralize gastric acid, taken 1 hr after meal effective for up to 2 hrs. Can affect absorption of drugs by direct binding or via increasing gastric pH.
Sodium bicarbonate What does it do? Brand names?
Reacts with HCl to produce NaCl and CO2 which causes belching and gastric distention. Baking soda, Alka Seltzer
Magnesium hydroxide & Aluminum hydroxide What does it do what are the brand names?
Maalox, Mytanta, Gelusil Reacts with HCl to form water and aluminum chloride or magnesium chloride. Magnesium salts not absorbed can cause osmotic diarrhea and aluminum salts can cause constipation so often used together.
H2 receptor antagonists
Cimetidine
Pharmaco kinetics of H2 receptor antagonists all but which one undergoes?
All but nizatidine under-go first pass metabolism resulting in 50% bioavailability. Cleared by both metabolism and excretion so need for dose reduction with severe renal dysfunction.
Pharmacodynamics of H2receptor antagonists
Highly selective H2 competitive antagonists which inhibit meal-stimulated but especially basal nocturnal gastric acid secretion and pepsin. Inhibit 60-70% of acid secretion per day.
H2 receptor antagonists AEs
Extremely safe, < 3% diarrhea, constipation, headache fatigue, myalgias In elderly in intensive care or renal or hepatic dysfunction- mental status perturbation Cimetidine inhibits binding of dihydrotestosterone to androgen receptors and estradiol metabolism so increases serum prolactin resulting in possible male gynecomastia or impotence and female galactorrhea. Cross placenta and excreted in breast milk
DIs of H2 antagonists
Competes with creatinine and with some drugs for renal tubule secretion Cimetidine inhibits P450 drug metabolism
Definitions of the 3 diseases of acid-peptic diseases

Factors that Protect (6) and Damage (9)

Parietal cell acid secretion

H. Pylori in Duodenal Peptic Ulcer Disease
What environment does it live in?
What does it do?
What does it produce?
What does this product cause?
What on the surface of this causes inflammation?

NSAIDS in Peptic Ulcer Disease
What type of inhibitor?
What type of inhibition is the biggest issue?
How does local injury happen?
Mortality?

Drugs used for Acid-peptic diseases
Drugs that reduce gastic acidity 3
and Mucosal protecting agents 3

Antacids 4
- Sodium Bicarb
- Calcium Carbonate
- Mg Hydroxide
- Aluminum hydroxide
H2 receptor antagonists 4 only need to know one
all are ___ except for?

PPIs
5
What types of drugs are these?

Mucosal Protecting Agents
3

Abx for the tx of helicobacter pylori-associated ulcers
4
only need to know 2

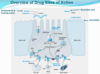
Overview of drug site of action
Laxative bulk forming

Bulk forming laxative 3

Stool Softeners
3

Osmotic Laxatives
4