Lymphatic System Flashcards
(68 cards)
The lymphatic system consists of lymph, ________________, lymphoid tissues and organs, and _________________
Lymphatics
Lymphocytes
The primary function of the lymphatic system is the production, maintenance, and distrubution of __________________
Lymphocytes
The lymphatic vascular system is a system of thin-walled endothelial channels that collect excess interstitial fluid from the tissue spaces and returns it to the blood as _____________
Lymph
Unlike the circulatory system, lymph flows in _______ direction towards the _________
One
Heart
At the _______________ end of the capillary microvasculature, the rate of tissue fluid generally exceeds fluid reuptake
Venous
At the venous end of the microvasculature, the blood pressure is ___________ (less than, greater than) that of the tissue fluid, forcing some fluid to return to the capillaries
Less than

Explain this figure.

At the arterial end of the microvasculature, blood pressure and hypertonicity is higher than that of the tissue fluid, forcing fluid out of the capillary and into the surrounding tissue; however, at the venuous end of the microvasculature, blood pressure and hypertonicity is lower than that of the tissue fluid, forcing fluid into the capillary
What happens to fluid that is not reabsorbed by capillaries?
Excess fluid is drained by lymph capillaries and converies into progressively larger lymphatic vessels
________________ __________ carry lymph from peripheral tissues
Lymphatic vessels
Lymphatic _____________________ originate in the various tissues and are thin, close-ended vessels that consist of a single layer of endothelium
Capillaries

Lymphatic capillaries converge into larger lymphatic vessels with structures similar to those of veins except that they have _______________ walls and lack a clear-cut separation between ________________
Thinner
Tunics

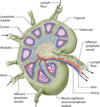
To what does the V point?

Lymphatic valve
Two sets of lymphatic vessels collect lymph. What are they?
Superficial lymphatics
Deep lymphatics
Lymphatic vessels ultimately end up as two large trunks. What are they?
Thoracic duct
Right lymphatic duct
The ______________ duct empties lymph into the junction of the left jugular vein with the left subclavian vein, accounting for 75%of all lymph drainage
Thoracic duct

The ___________ duct empties into the confluence of the right subclavian fvein and the right internal jugular vein, accounting for approximately 25% of lymph collection
Right lymphatic duct

What are some characteristics of lymphoid tissues?
They are composed of connective tissues and contain a rich supply of lymphocytes
Lymphoid tissues are composed of ____________ and a rich network of reticular or _____________ fibers supporting lymphocytes
Free cells
Type III collagen
Reticular fibers in lymphoid tissues are produced by fibroblast-derived cells called ________________ _______________
Reticular cells
In lymphoid tissues, fibroblast-like reticular cells produce and secrete reticulin fibers to which many cells loosely attach, including ____________ and __________________
Macrophages
Lymphocytes
What is the largest lymphoid organ?
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) can be found in what types of sites?
Sites exposed to the external environment
What are two specific types of MALT discussed in class?
Tonsils
Peyer’s patches (GI)
The _____________ are large nodules in the walls of the pharynx of which most people contain five
Tonsils