Lecture 20 - Female Reproductive System Flashcards
Gonads
both systems have primary sex organs called gonads
• produce sex cells called gametes
- > Oocytes in females
- > sperm in males
• both systems have ducts to transport gametes from gonads to site of fertilization
Perineum
diamond-shaped region between thighs with the following boundaries:
- > pubis symphysis
- > ischeal tuberosities
- > coccyx
Subdivided into…
- Urogenital triangle
- Anal triangle

Urogenital triangle vs Anal triangle
Urogenital triangle
- > anterior
- > ischial tuberosities and pubis symphysis
Anal Triangle
- > posterior
- > ischial tuberosities and coccyx

Primary vs Accessory female reproductive organs
Primary
- > ovaries
Accessory
- > Uterine/fallopian tubes
- > uterus
- > vagina
- > mammary glands
Pouches of female reproductive system
*formed from peritoneal folds around pelvic organs*
- Vesicouterine pouch
- > anterior space between the uterus and urinary bladder - Rectouterine pouch
- > posterior space between the uterus and the rectum

Anchoring ligaments of the ovaries; how is it anchored within the pelvic cavity
*anchored within pelvic cavity by several folds of peritoneum*
- Broad ligament
- Ovarian ligament
- Suspensory ligament

Structures/layers of the ovary
- > each ovary is surrounded by an epithelial layer of simple cuboidal cells called the germinal epithelium
- > deep to the GE is a connective tissue capsule called the tunica albuginea
- > deep to TA, the ovary can be divided into an outter cortex and an inner medulla

Cortex and medulla of the ovary
- > the cortex contains ovarian follicles
- > medulla contains connective tissue, blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerves

Ovarian follicles
- > thousands are found within the cortex of ovary
- > OF consist of oocytes surrounded by follicle cells
- > several different types of ovarian follicles, each representing a different stage of development
Stages of follicle development
- Primordial follicle
- Primary follicle
- Secondary follicle
- Vesicular follicle
- Corpus luteum
- Corpus albicans
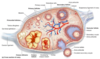
Primordial follicle
- > most primative type
consists of…
- > a primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of squamous cells

Primary follicle
consists of..
- > primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of cuboidal cells
Secondary follicle
consists of…
- > a primary oocyte, many layers of granulosa cells and a fluid-filled space call an antrum
- > 2 protective structures surround the primary oocyte
* Zona pellucida (outside)
* Corona Radiata (inside)
* antrum

Antrum
contains serous fluid that increases in volume as ovulation nears
- > protective/nutritional fluid
Protective structures surrounding the primary oocyte
- Zona pellucida (outside)
- Corona Radiata (inside)

Vesicular follicle
aka. mature follicle or Graafian follicle
consists of…
- > secondary oocyte surrounded by zona pellucida and corona radiata
- > an enlarged antrum
- > many layers of follicle cells
- > walls of follicle merges with ovarian wall and eventually releases the follicle into a uterine tube

Corpus luteum
- > following ovulation, the remnants of the follicle (not including the oocyte) becomes the corpus luteam
- > CL secretes progesterone and estrogen, which stimulate the growth of the uterine endometrium

Ovulation
- > the membrane of the vestibular follicle fuses to the ovarian membrane
- > the follicle ruptures and releases the oocyte into the fimbrea/uterine tube
Corpus Albicans
- > corpus luteum degrades itself into the corpus albicans
- > the corpus albicans is scar tissue that doesn’t secrete anything (estrogen or progesterone)

Characteristics of uterine tubes and oocyte travel
- > extends laterally from both sides of the uterus
- > around 10-12cm in length
- > covered in mesosalpinx (part of broad ligament)
- > the secondary oocyte is usually fertilized in the lateral part of fallopian tube (pre-embryo)
- > takes the pre-embryo around 3 days to travel the length of uterine tube and reach the lumen of the uterus
Regions of the uterine tubes
Infundibulum - > lateral opening of the tube, encircled by fimbriae (fingers)
Ampulla - > expanded region medial to infundibulum where fertilization typically occurs
Isthmus - > medial to the ampula and represents 1/3 of the entire length of UT
Uterine part - > contiuous with the uterus

Walls of the uterine tubes
- Mucosa - > cilliated (movement) columnar epithelial cells
- Muscularis - > innter circular layer and outer longitudinal layer of smooth muscle
- Serosa - > external serous membrane covering uterine tube
*no submucosa - > does not need to secrete anything*

Characteristics of uterus
- > pear-shaped, thick-walled muscular organ within pelvic cavity
- > possesses a lumen that is superiorlaterally continuous with the uterine tubes and inferiorly contiuous with vagina
functions of uterus
- > site of implantation
- > supports and protects the developing embryo/fetus
Anteverted vs Retroverted Uterus
Anteverted (normal)
- > angled anterosuperiorly
- > projected towards body cavity
Retroverted
- > projected towards rectum
regions of the uterus
- fundus
- body
- isthmus
- Cervix

What supports the uterus
several structures
- > muscles of the pelvic floor
- > round ligaments
- > transverse cervical ligaments (cardinal ligaments)
- > uterosacral ligaments (sacrocervical ligaments)
What can happen if the uterus isn’t properly supported/ there is a weakness in the support system
can result in prolapse, in which uterus protrudes through the vagina

How does blood get to the uterus
uterine arteries
- > which are branches from the internal iliac arteries
Layers of the uterine wall
- Perimetrium
- > outermost layer is a serousal layer of connective tissue - Myometrium
- > thick, middle tuni comprised of smooth muscle - Endometrium
- > mucosa composed of a simple columnar epithelium and an underlying lamina propria
Lamina propria
found within the endometrium, the lamina propria is filled with uterine glands, which enlarge during the uterine cycle
Layer of the endometrium
- Functional layer (stratum functionalis)
- > changes thickness depending of the phase of the uterine cycle shed during menses - Basal layer (stratum basalis)
- > deeper layer immediately adjacent to myometrium and is perminant (undergoes little/no change during the uterine cycle)

Phases of the menstrual cycle
Mentrual phase (0-4) - > sheds functional layer
Proliferal Phase (5-14) - > follicle matures and functional layer builds up
Ovulation - > day 14
Secretory Phase (15-28) - > secretes progesterone and estrogen
Prementrual phase (26-28)

characteristics of the vagina
- > fibromuscular tube about 10cm long that connects the uterus to the outside of the body
- > has 3 tunics
- > opening of the vagina is called the vaginal orifice
- > near the opening, folds of the mucosa form a membranous barrier called the hymen
Wall of the vagina
distensible wall consisting of 3 layers
- inner mucosa
- middle muscularis
- outer adventitia
Mammary glands
- > modified integumentary glands that secrete breast milk
- > divided into lobes - > subdivided into lobules
- > milk drains into lactiferous ducts which is stored into lactiferous sinusses
- > supported by suspensary ligaments by attaching the skin of the gland to the pectoralis major
Nipple vs areola
Nipple
- > cylyndrical projection on the center of the breast containing multiple openings from internal secretory ducts
Areola
- > pinkish/brown pigmented ring of skin that surrounds the nipple
Ectopic pregnancy
embryo attaches outside of uterus


