Gram Positive Cocci Flashcards
Most common Staphylococcal isolate in dogs
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
Disease and Cause

Ulcerative pododermatitis
Staphylococcus aureus
Disease and Cause

Jowl Abscess
Streptococcus porcinus
Disease and Cause
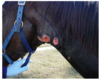
Strangles
Streptococcus equi subsp equi
Guttural Pouch Empyema
Accumulation of purulent material in guttural pouch
_____________________
Secondary to Strangles infection
Clinical sign of Strangle infection appear __________ after exposure
Clinical sign of Strangle infection appear 3-14 days after exposure
Diagnosis of Staphylococcal Infection
Direct Examination
Culture
PCR
Cause

Streptococcus suis
___________ is one of the most common nosocomial pathogens in humans.
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most common nosocomial pathogens in humans.
Guttural Pouch Chondroids
Accumulation of soft or hard concretions in one or both guttural pouches
______________________
Secondary to Strangles infection
Enterococcus sp inhabit the
GI tract
Enteroccous infections cause
persistent UTI
Serotype 2 of Streptococcus ________ is the most common isolate.
Serotype 2 of Streptococcus suis is the most common isolate.
First clinical sign to appear from a Strangles infection
Fever
__________________
39 - 39.5 C
Disease and Cause

Scarlet Fever
Streptococcus pyogenes
Causes Scarlet Fever in humans
Streptococcus pyogenes
Staphylococcal isloate that causes mastitis in cattle
Staphylococus aureus
Causes ulcerative pododermatitis in sheep and humans
Staphylococcus aureus

Staphylococcus sp
Structure of Streptococcus sp.
Pairs or chains
Problems associated with treating Staphylococcal infections
Reisistance!
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing is critical
___________________
Clindamycin, Macrolide, Methicillin
Classification of S. equi subsp equi
Beta-hemolytic, Group C
For an animal to be removed from quarantine after a Strangles infection, they must have
For an animal to be removed from quarantine after a Strangles infection, they must have 3 negative cultures at weekly intervals
Age of horses typically infected with Strangles
< 2 years old
Stapylococcal isolate that causes chronic pyogranulomatous inflammation inf rodents, equines and humans
Staphyloccus aureus
Streptococcus agalactiae/dysgalactiae/equi subsp zooepidemicus/uberis cause
Mastitis
Reportable Streptococcal disease
Streptococcous equi subsp equi - Strangles
Disease and Cause

Greasy Pig Disease
Staphylococcus hyicus
S. equi subsp equi should be distinguished from:
S. equi zooepidemicus
S. dysgalactae equisimillis
Treatment of Staphylococcal Infections
Cephalosporins (1st generation)
Quinolones
Chloramphenicol
Aminoglycoside
Causes exudative epidermitis and Greasy Pig Disease
Staphyloccus hyicus
Causes Bumble Foot in Birds
Staphylococcus aureus
Are foals less than 4 months old more susceptible to Strangles infection?
No, protected by maternal antibodies
Causes cervical lymphadenitis in sheep
Staphylococcus aureus subsp anaerobius
Disease and Cause

Acute fulminating septicemia
Streptococcus iniae
Streptococcus canis causes
Septicemia and embolic lesions in the heart and lungs of puppies and kittens
Virulence factors of Streptococcus equi subsp equi
Hyaluronic acid capsule
M Protein
IgG binding protein
PG/Techoic Acid
Streptokinase
Hyaluronidase
Streptolysin S
DNAase
Pyrogenic exotoxin
Diagnostic test for Streptococcus equi subsp equi
Culture
Serology
PCR
Streptococcal species are classified by
Streptococcal species are classified by hemolytic activity
Natural habitat for Staphylococcus sp.
Skin and mucous membranes
Habitat for Streptococcus sp.
Oral cavity, nasopharynx, skin, GI and gential tracts
Disease and Cause

Bumble Foot
Staphylococcus aureus
Causes jowl abscesses in pigs
Streptococcus porcinus
Virulence factors of Staphylococcus sp
Protein A
Hemolysins
Proteases
Hyaluronidase
Lipases
Alpha Toxins
Leukocidin
Exfolative Toxins
Biofilm
Coagulase
Enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin
Virulence Factors of Streptococcus
Hemolysins
Exotoxins
Capsules
PG/Techoic/Lipotechoic Acid
M Protein
Ig Binding Protein
Streptokinase
Pyrogenic Exotoxins
Causes acute fulminating septicemia in fish
Streptococcus iniae
Treatment of Streptococcus equi subsp equi
Symptomatic
ABX only if abscess has not formed yet (PenG, Potenated Sulfas)
Collateral Damage
Ecological adverse effect of antibiotic therapy; selection of a drug resistant organism and unwanted development of colonization or infection iwth multi drug resistant organism

Streptococcus sp
Disease and Cause

Mastitis
Staphylococcus aureus
Causes Strangles in horses
Streptococcus equi subsp equi
Cause

Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
Lymph node absesses occur ____________ after initial signs of Strangles infection.
Lymph node absesses occur within 2 weeks after initial signs of Strangles infection.


