Anaerobic Bacteria Flashcards

Fusobacterium necrophorum

Clostridium piliforme
__________ is a common predisposing faxtor for and host response to Clostridial infection.
Necrosis is a common predisposing faxtor for and host response to Clostridial infection.
Diagnose Clostridium septicum
Direct Fluorescent antibody staining
Pathogenesis of Clostridium chauvoei
Exogenous infections occur through wounds → Result in anaerobic environement → Deposited endospores germinate and multiply → Toxins elaborated during growth cause more tissue destruction → Fermentation of muscle glycogen results in gas accumulation → Metabolic end products have distinctive smells
Cause and Disease

Clostridium tetani
Tetanus
Diagnosis of anaerobic, non spore forming, gram negative rods
PCR

Clostridium tetani

Clostridium difficile
Virulence factor of Fusobacterium necrophorum
Leukotoxin
Clostridium piliforme is an obligate (intra/extra)-cellular pathogen
Clostridium piliforme is an obligate (intra/extra)-cellular pathogen
Descending tetanus occurs in (more/less) susceptible animals.
Descending tetanus occurs in (more/less) susceptible animals.
Early symptoms of infection in mammals involve hind limb paralysis, skeletal muscle paralysis leads to respiratory failure.
Clostridium botulinum
Exogenous, causes gas gangrene and Big Head in rams
Clostridium novyi, Type A
Diverse group of organisms with toxin types A-G. Toxin type determines the species affinity, causes botulism
Clostridium botulinum
Clostridium _____ toxin causes enterotoxemia, pulp kidney disease and overeating disease
Clostridium D toxin causes enterotoxemia, pulp kidney disease and overeating disease
Causes symmetrical flaccid paralysis
Clostridium botulinum
Cause and Disease

Clostridium botulinum
Botulism
Produce black iron porphyrin pigments
Porphyromonas spp
Prevotella spp
___________ is contraindicated in horses for treatment of Clostridium difficile.
Clindamycin is contraindicated in horses for treatment of Clostridium difficile.
Why can’t you use aminoglycoside antibiotics for anaerobic infections?
Aminoglycoside transport mechanisms require oxygen.
Cause
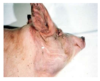
Clostridium septicum
Cause

Clostridium perfringens
Cause and Disease
(Rear Leg Paralysis)

Clostridium botulinum
Botulism







