Female Repro Flashcards
What gnes promote ovarian development vs testerone?
DAX-1 gene promotes ovarian development and differentiation
SRY gene coding for TDF which upregulates Sox9 expression for testicular development
Intersex
Intersex is a general, nonspecific term meaning that ambiguous genitalia are present, but does not indicate the nature or etiology of the abnormality
Sexual development disorders are categorized as:
Abnormalities of chromosomal sex
Abnormalities of gonadal sex
Abnormalities of phenotypic sex
Abnormalities of chromosomal sex
Animals with these disorders have an abnormality in the number or structure of the sex chromosomes
◦ XXY → Klinefelter
◦ XXX
◦ XO → Turner
◦ XX/XY (Chimeras and mosaics)
In general, animals with trisomy or monosomy have underdeveloped genitalia and are sterile

An example of these chromosomal sex disorders are male tortoiseshell or calico cats; they have testicular hypoplasia and are almost always infertile ( some may be XXY)
Chimeras
individuals composed of two or more cell populations each arising from different individual
Mosaics
individuals composed of two or more cell populations, but the cells originate within the same individual
What is the most common example of a chimera?
Genetic female born co-twinwithamale
Pathogenesis → vascular anastomoses between placentas allow male hormones (incl Mullerian Inhibitory Substance) and cells to cross and suppress development of the female genital system
Macroscopically, freemartins have small ovaries, blind- ended uterus, poorly developed vagina, enlarged clitoris and seminal vesicles
Maletwinisminimallyaffected
Abnormalities of gonadal sex
True hermaphrodites
How do you define them?
Ovary and testis present in the same individual
Lateral → testis one side, ovary the other
Bilateral → ovotestes both sides
Unilateral → ovotestis one side, ovary or testis on other
Ambiguous external genitalia
Rare, seen more in dogs, goats and pigs

True hermaphrodite
mix of male and female

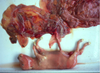
Gilt, lateral hermaphrodite (testis one side, ovary the other)

True hermaphrodite → Ovotestis
Bilateral
Sex reversal
Sex reversal; animal in which gonadal sex does not follow chromosomal sex
Gonad is not the type corresponding to the XX or XY makeup of the individual
◦ American Cocker Spaniel
Dogs with XX sexual reversal may be XX true
hermaphrodites or XX males
◦ Polled goats (gene with Y effect close to gene for hornlessness)
pseudohermaphroditism
Abnormalities in phenotypic sex (pseudohermaphroditism)
Occur when chromosomal and gonadal sex agree, but the internal or external genitalia are ambiguous
Female pseudohermaphrodites
Often the result of iatrogenic administration of androgens or progestagens during gestation
Male pseudohermaphrodites
Due to failure of Mullerian duct regression
Persistent Mullerian Duct Syndrome in the Miniature Schnauzer

XY dog with testes- Clitoral enlargement The clitoris protrudes between the labia and is visible on the ventral floor of the vulva
Segmental aplasia of the paramesonephric ducts
DEVELOPMENTAL ANOMALIES of Phenotype Sex
Segmental aplasia of the paramesonephric ducts Failure of short or long segments of the uterine horn to
develop
Complete absence of an entire horn → uterus unicornis
Commonly found in white Shorthorn cattle → “white heifer disease” → associated with the recessive gene for white coat color

Uterus unicornis

Uterus unicornis; ovaries on both sides
Imperfect fusion of the paramesonephric ducts
Results in double vagina, double cervix, and uterus
didelphys

Uterus didelphys

double cervix
Failure of fusion of the paramesonephric ducts with the urogenital sinus
Persistence of a tissue band running across the vagina just cranial to the opening of the urethra (imperforate hymen)

Imperforate hymen