Eye and Eye Movements Flashcards
1
Q
- What bones make up the orbit?
A
- Frontal
- Ethmoid
- Sphenoid
- Zygomatic
- Lacrimal
- Maxillary
2
Q
- What structures pass through the optic canal?
A
- CN II (Optic N)
- Opthalmic a.
3
Q
- What passes through the superior orbital fissure?
A
- CN III (Oculomotor n.)
- CN IV (Trochlear n.)
- CN VI (Abducens n.)
- V1 from CN V (Trigeminal)
4
Q
- What passes through the inferior orbital fissure?
A
- Maxillary n. as it turns into infraorbital n.
- Infraorbital a.
- Zygomatic n.
5
Q
- Sinus relationships to orbit
A
- Frontal-superomedial to orbit
- Ethmoid-medial to orbit
- Maxillary-inferior to orbit
- Sphenoid-posteromedial to orbit

6
Q
- Orbital Blow Out Fractures
A
- Fracture of orbital walls usually from indirect trauma
- Typically occurs medially and inferiorly-involving the maxillary bone
- Orbit contents may prolapse and trap in maxillary sinus
- Sx
- Diplopia
- Globe ptosis
- Exapthalmos
7
Q
*

A
- Axis of obrit
- Optical axis
8
Q
- What are the movements of the pupil along a vertical axis?
A
- Abduction
- Adduction
9
Q
- What are the movements of the pupil along a horizontal axis?
A
- Elevation
- Depression
10
Q
- What are the movements about the AP (Visual Axis)?
A
- Intorsion (medial rotation)
- Extorsion (lateral rotation)
11
Q
- Identify the extraocular muscles

A
- Superior oblique m
- Levator palpebrae superioris m.
- Superior rectus m.
- Medial rectus m.
- Lateral rectus m.
- Inferior oblique m.
- Inferior rectus m.
12
Q

A
- Oculomotor N (CN III)
- Oculomotor N (CN III)
- Abducent N (CN VI)
- Elevates superior eyelid
- ABducts. depresses, and medially rotates eyeball
- ABducts, elevates and laterallyrotates eyeball
- Elevates, ADducts and rotates eyeball medially
- Depresses, ADducts, and rotates eyeball laterally
- ADduct eyeball
- ABducts eyeball
13
Q
- Extraocular muscles and their movements
A

14
Q

A
- Inferior oblique
- Superior rectus
- Lateral rectus
- Medial rectus
- Superior oblique
- Inferior rectus
15
Q

A
- Superior rectus and inferior oblique
- Superior oblique and inferior rectus
16
Q

A
- Superior rectus
- Inferior oblique
- Medial rectus
- Lateral rectus
- Inferior rectus
- Superior oblique
17
Q
- When the eye is ABducted by the lateral rectus, only the _ muscles can produce elevation and depression
- When the eye is ADducted by the medial rectus, only the _ muscles can produce elevation and depression
A
- Rectus
- Oblique
18
Q
- Muscles are trapped from performing their function when the visual gaze is _ to muscle fiber direction
A
- Perpendicular
19
Q

A
- Superior rectus (III)
- Lateral rectus (VI)
- Inferior rectus (III)
- Inferior oblique (III)
- Medial rectus (III)
- Superiior oblique (IV)
20
Q

A
- Supratrochlear n.
- Nasociliary n.
- Supraorbital n.
- Lacrimal n.
- Frontal n.
- V1 Opthalamic N
21
Q

A
- Oculomotor n.
- Parasympathetic root of ciliary ganglion
- Inferior branch of oculomotor n.
- Superior branch of oculomotor n.
22
Q

A
- Trochlear n.
- Oculomotor n.
- Trochlear n.
- Abducent n.
23
Q

A
- Supratrochlear n.
- Nasociliary n.
- Supraorbital n.
- Lacrimal n.
- Frontal n.
- V1 Opthalamic n.
24
Q
- What nerves do NOT go through tendinous ring of the extraocular muscles?
A
- Frontal N
- Lacrimal N
- Trochlear n
25
* ***What muscles DO go through the tendinous ring of the extraocular muscles?***
* Optic nerve
* Trochlear n
* Oculomotor n (superior and inferior division)
* Nasociliary n
* Abducent n
26
Presynaptic sympathetic neurons synapse in _ ganglion before traveling with neurovascular structures to their target organ
* Superior cervical ganglion
27
* Parasympathetic fibers travel to what areas of the eye
* Sphincter pupillae
* Ciliary muscle
28
* Sympathetic fibers travel to what areas of the eye
* Dilator pupillae
* Superior and inferior tarsal muscles
29
* Sensory fibers travel from which areas of the eye to the brain
* Cornea
* Choroid
* Iris
30
* ***Trochlear Palsy***
* Superior oblique m is not working in affected eye
* Person cannot ABduct, depress, or medially rotate eye
* Head tilts away from affected side
* Diplopia worsens on downward gaze
*

31
* ***Abducens Palsy***
* Damage to CN VI (Abducens N)
* Abducens n innervates lateral rectus m
* Cannot ABduct eye on affected side

32
* ***Down and Out Eye***
* D/t loss of ocular muscle innervation (oculomotor n)
* SO and LR muscles still intact (since superior oblique is innervated by the trochlear n. and lateral rectalis m is innervated by the abducens n (CN VI)
33
* ***Complete Ptosis***
* Loss of innnervation to levator palpebrae superioris (Oculomotor n. CNIII)
* Can't open eyelid
34
* ***Pupil dilation***
* Loss of parasympathetic innervation to the pupil
35
* ***Horner Syndrome (This was in like 4 different lectures, so probably high yield)***
* Miosis (Constriction of Pupils)
* Anhydrosis
* Ptosis
* Redness and increased temp of skin (vasodilation)
* Loss of sympathetic innervation
36
* ***Describe the pupillary light reflex***
1. Light sensed by CN II (**Optic N)** and synapses in pretectal nucleus
2. Cells from pretectal nucleus will synspase in Edinger Westphal nucleus
3. Preganglionic parasympathetic neurons will travel with CN III and synapse in the ciliary ganglion
4. Postganglionic parasympathetic fibers will synapse in the pupillary constrictor m.

37
* ***Describe the corneal reflex (like when someone touches your eyeball with a cuetip)***
1. Receptors in cornea detect touch or irritation
2. Travel in CN V (Trigeminal n) and synapse in trigeminal sensory nucleus or spinal trigeminal nucleus
3. Cells from trigeminal nuclei project to facial nucleus
4. Neuron in facial n will cause the eye to blink

38
* What compromises the fibrous layer of the eyeball?
* Sclera
* Cornea
39
* What makes up the vascular layer of the eyeball?
* Choroid
* Ciliary Body
* Iris
40
* What makes up the inner layer of the eyeball
* Retina
41
* True or false-the optic nerve is surrounded by the meninges (dura, arachnoid, and pia mater layers)?
* True
42
* What important structures travel WITHIN the optic nerve
* Central retinal v
* Central retinal a
43
* Palprebra conjunctiva lines the \_
* Bulbar (ocular) conjunctiva lines the \_
* Innermost part of the eyelids
* Outermost part of the eyeball
44
* The following image shows inflammation in which conjunctiva of the eye?
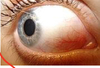
* Bulbar conjunctiva
45
* The following image shows inflammation in which conjunctiva of the eye?

* Palpebral
46
* The _ muscle is innnervated by the sympathetic nervous system and aids the Levator palpebrae superioris in raising the eyelid
* Superior tarsal m. (Muellers m.)
47
* The _ muscle is innervated by the oculomotor n (CN III) and functions to gently close the eyelid
* Orbicularis oculi m.
48
* What condition is shown in the following image? Describe characteristics

* **Subconjunctival hemorrhage**
* ****Below bulbar layer of conjunctiva and sclera
* Rupture of vasculature
* Can occur from increased ocular pressure d/t
* Coughing
* Vomiting
* Valsalva maneuver
49
* ***Complete Ptosis***
* Damage to levator palpebrae superioris
* Innervated by GSE fibers of CN III (Oculomotor
* Desctruction of CN III or one of its branches to this muscle results on paralysis of the levator palpebrae superioris m and complete ptosis

50
* ***Partial ptosis***
* **Damage to Tarsal m (Muller)**
* Innervated by **postganglionic sympathetic fibers** (these fibers originate at T1)
* **Horner's Syndrome usually involves paralysis of tarsal muscles******
51
* What condition is shown in the following image

* Bulging optic disc
* EMERGENT-this is caused by an increase in intracranial pressure (need to find the source of this ASAP)
52
* ***Arterial Supply of the Eye***

53


54
* Infections from the face can drain via venous system into the \_
* Cavernous sinus
55
* ***The following image shows occlusion of which vascular structure?***
* ***What can cause this?***

* Central retinal vein
* Causes:
* Increased intracranial pressure
* Hardening of Central retinal a.
* Hemorrhages
* Dilated Veins
56
* ***The following image shows occlusion of what vascular structure?***
* ***What can cause this?***

* Central retinal a. (BAD-occlusion of this artery will cause blindness since it is the ONLY source of arterial blood supply to the retina)
* Causes
* Atherosclerosis
* Embolism
* Characteristics
* * Retina appears white
* Cherry red spot
* Veins and As attenuated
57
* Describe the pathway of tears from the lacrimal apparatus
* Lacrimal gland
* Lacrimal canaliculi
* Lacrimal sac
* Nasolacrimal duct
* Inferior meatus of nose (why your nose runs when you cry a lot when you're studying for neuro)
58
* The lacrimal part of the _ muscle contracts to open the lacrimal sac to bring more tears into the lacrimal sac
* Orbicularis oculi m.
59
* What is the purpose of the lacrimal gland?
* Nourish cornea and conjunctiva

60
* ***Describe the steps of tear production***
1. Greater petrosal n. (Branch of CN VII) and deep petrosal n. form nerve of pterygoid canal.
2. Parasympathetic fibers synapse in pterygopalatine ganglion
3. Travel with V2, then with the zygomatic branch, communicating branch, and finally, the lacrimal n. of V1

61
* What are the chambers of the eye
* Ciliary body
* Ciliary process
* Anterior chamber
* Posterior chamber
62
* Ciliary body
* Circumferential tissue inside eye
* Composed of ciliary muscle and ciliary processes
63
* Ciliary processes
* Secrete aqeuous humor that fills anterior and posterior chambers
64
* Anterior chamber
* Space between cornea and iris/pupil
65
* Posterior chamber
* Space between iris/pupil and the lens and cilliary body
66
* ***Flow of aq humor***
1. Ciliary process
2. Posterior chamber
3. Anterior chamber
4. Scleral venous sinus (drains aqueous humor)
67
* ***Blockage of the scleral venous sinus (Schlemm's canal) can lead to increased intraocular pressure and what medical condition?***
* Glaucoma
68
* ***Hyphema***
* Pooling of blood in anterior chamber of eye
* (remember that the anterior chamber of the eye is the space between the cornea and iris/pupil)
69
* Contraction of the ciliary muscles _ size of the ciliary body
* _ tension on suspensory ligament
* Lens becomes more _ (for near vision)
* Decreased
* Decreases
* Round


